Introduction:
This blog explains about the Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) feature.
What is HSRP?
HSRP stands for Hot Standby Router Protocol. This is a Cisco proprietary protocol. HSRP is a next hop redundancy protocol. This protocol plays a key role on the Layer 3 high availability.
Why HSRP?
Routers or the Layer 3 devices acts as the next hop/gateway for the end point devices. When this next hop/gateway IP goes down for some reason, all the end points connected to that network will have no connectivity to other networks like Internet and Intranet.
HSRP feature provides redundancy on the next hop/gateway and assures High availability of service.
Before stepping into this, let’s understand how a network looks like without next hop redundancy protocol.
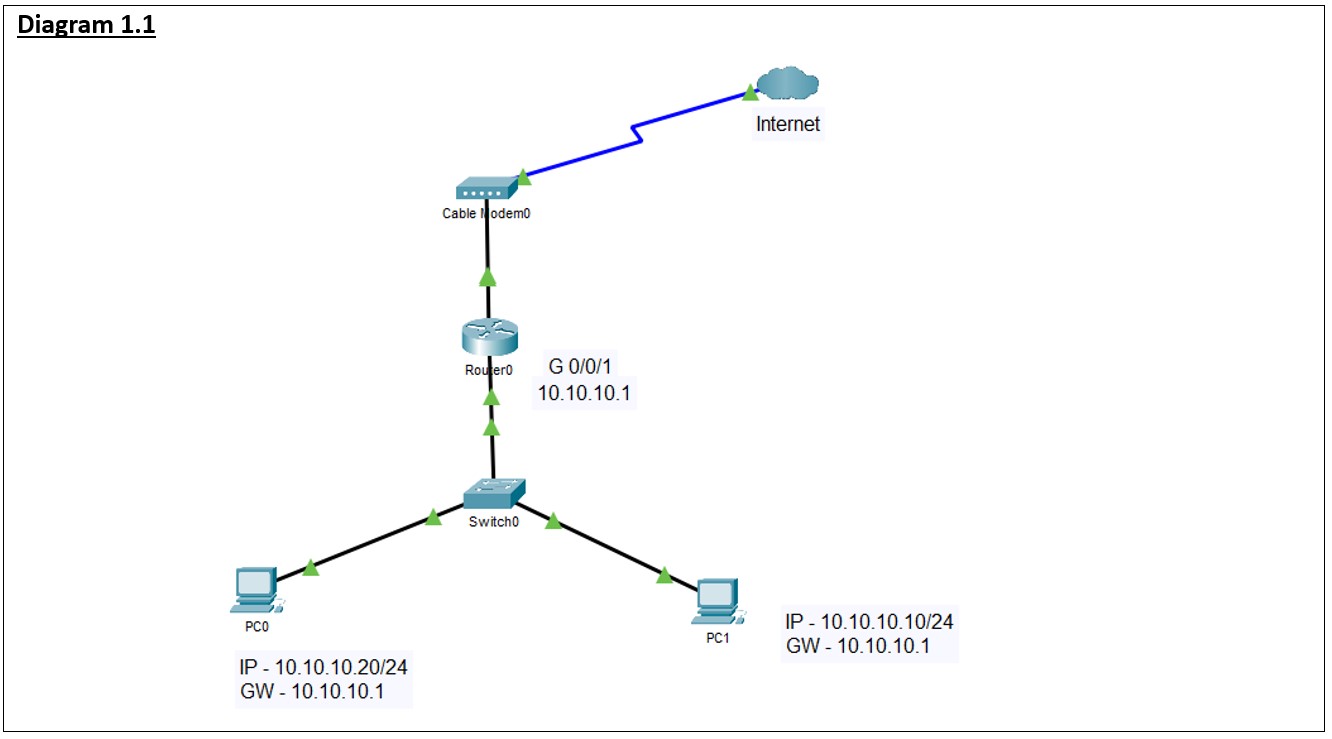
Scenario: Network without HSRP
The diagram 1.1 is a working network topology without HSRP. The PC are configured with the gateway as 10.10.10.1 (next hop) which is the layer 3 Interface of the Router#0. All the Internet traffic from the PC will e routed to the GW IP address 10.10.10.1.
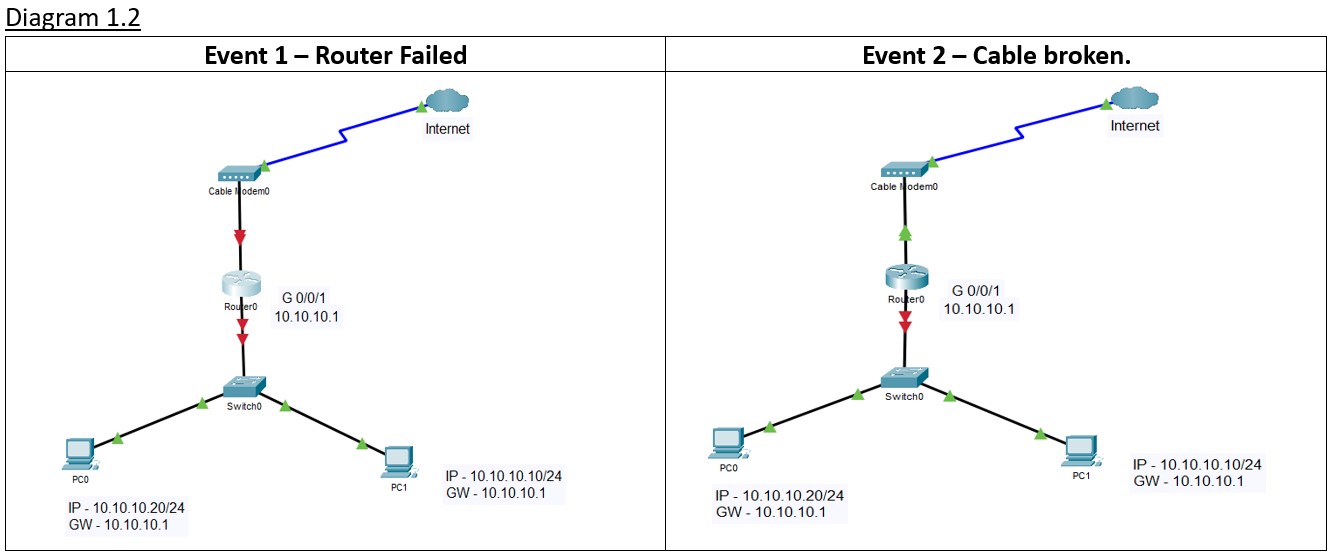
a) Event 1 – In the event of the router power failure or Crash, the gateway IP address 10.10.10.1 will not be available for the PCs and resulting in no connectivity to the Internet. (diagram 1.2)
b) Event 2 – In the event of the cable broken connecting from the switch to Router’s G 0/0/1, the gateway IP address 10.10.10.1 will not be available for the PCs and resulting in no connectivity to the Internet. (diagram 1.2)
How does HSRP works?
Scenario: Network without HSRP
The diagram 1.3 is a network topology with HSRP. In this scenario we have 2 Layer 3 devices (Router#0 and Router#1).
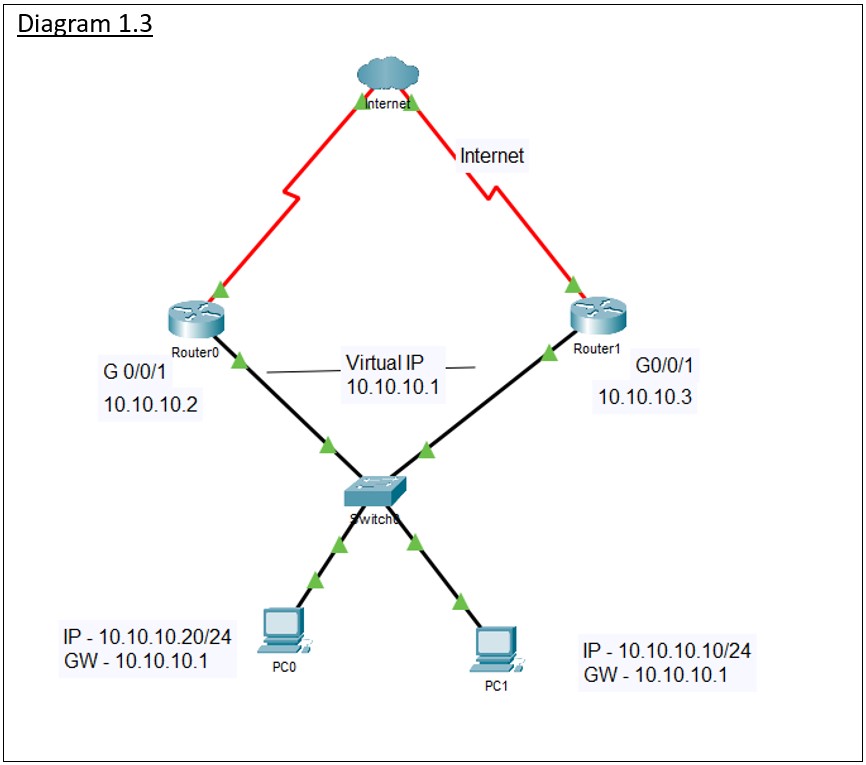
Step-by-Step Explanation:
1. Each router physical interface will be configured with an IP address on the same subnet and a Virtual IP address will be configured.
2. One router will be configured to be master and other one will be on standby.
3. The master router will own the virtual IP address.
4. Both, these routers will share hello messages with each other, thru a specific multicast packet.
5. In the event of the master router failed or the cable is broken, the standby router will not receive the hello message.
6. At this stage the standby router picks the virtual IP address and owns it.
7. The end points (PCs, Phones, Servers etc) will still see the availability for their gateway IP address and forwards the traffic.
Conclusion
In today’s advance technologies like Software defined networks, SD-WANs, Cloud environments still this HSRP protocols are running in the underlaying topology.


