Introduction:
This blog explains about Policy Based Routing.
What is a Policy Based Routing?
In general, a layer 3 device takes routing decision based on the route look up in the routing table. Policy Based Routing is a feature thru which an administrator can influence the IP routing decision in a Router or Layer 3 switch before the routing table-based routing.
Why Policy Based Routing?
When an network administrator decide to influence a router’s routing decision of a packet it received, policy based routing help.
What is Layer 3 in network?
Layer 3 is the IP packet in the OSI reference model. The routers and layer 3 devices handle IP packets. (Switches handles layer2 frames. Yes, when you say layer 2 it should be referred as frames)
IP Packet: The IP packet contains the following information on its header.
- Source IP address.
- Source port Number.
- Destination IP address.
- Destination port number.
- Destination service such as TCP or UDP.
The following figure 1.0 demonstrates the high level of an IP Packet Header field. Though there are several fields on the IP Packet Header, in the interest for the IP routing concept, the diagram is limited to the above mentioned five fields.
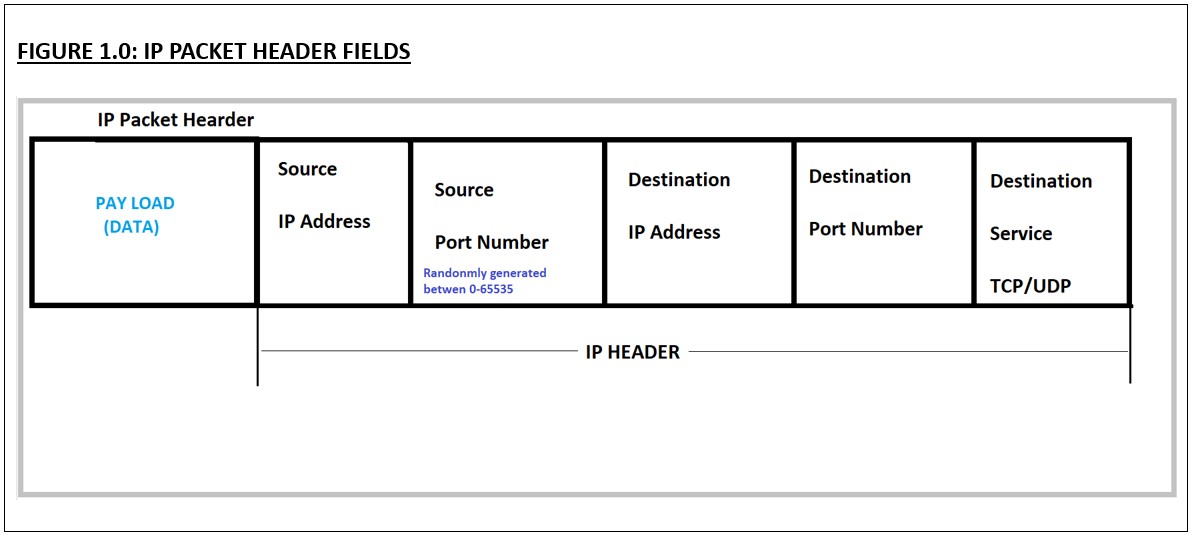
I hope the above diagrams gave basic idea of a packet header.
The following figure 1.1 is a simple network topology in which 2 PCs accessing a Web Application of the Organization located geographically on another site having two paths thru Router1 and Router2.
FIGURE 1.1: PACKET FLOW IN POLICY BASED ROUTING
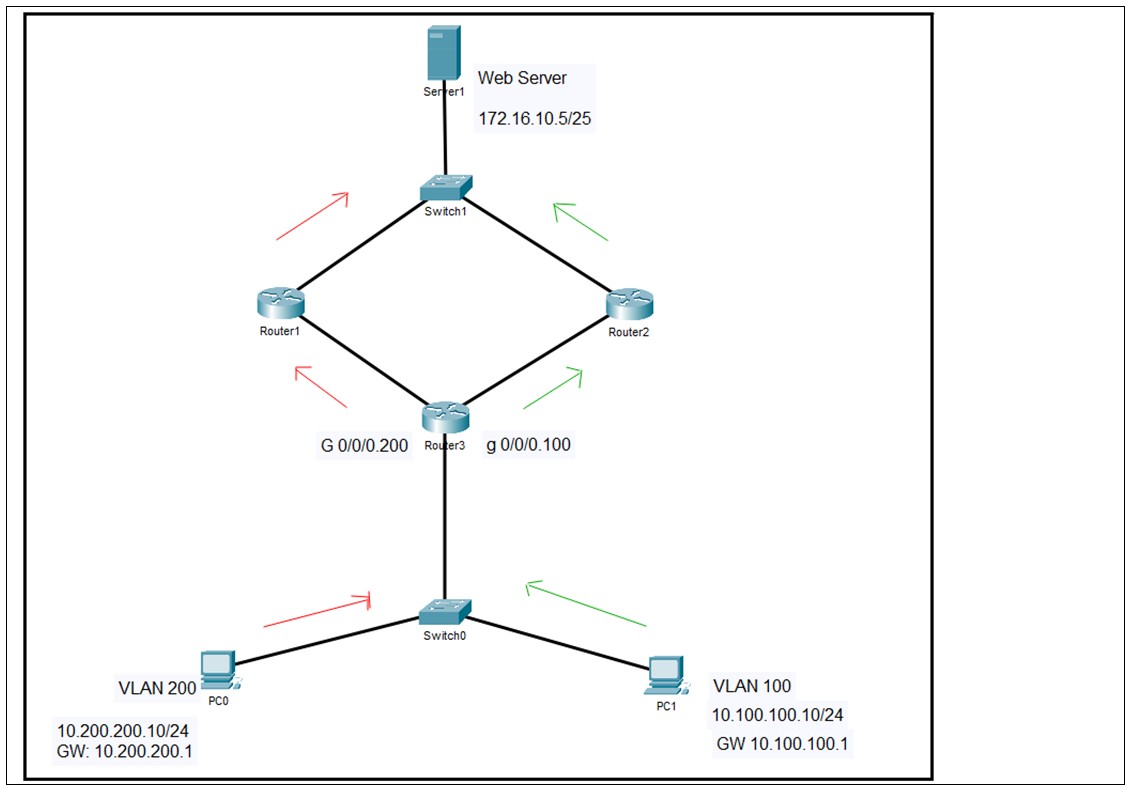
- Router3, Switch0, PC0 and PC1 belongs to Site-A.
- Router1, Router2, Switch1 and the Web Server belongs to Site-B
How does PBR Works?
- If we use a usual or general method of routing, only one WAN link (Links between R3-R1 and R3-R2) can be used at a time other might be idle or unused.
- Now, business has decided to use both the links.
- Business has decided that users in vlan 100 should go thru Router2 to reach the web application, and.
- Users in vlan 200 should go thru Router1 to reach the web application.
- This way both the WAN links can be utilized.
Let’s see how this can be achieved.
- Basically, any router or layer3 device will ONLY look into the destination IP address of the packet to take the routing/forwarding decision.
- Whereas thru Policy based forwarding we can influence this decision.
- Policy based forwarding will not only look into the destination IP address of the packet, it also looks into the source IP address and destination port of the packet and forward the packet to the mentioned next hop.
- PBR requires an access control list (ACL). This is to select the required source and destination IP of the packet.
- Then, map the ACL into a Named policy-based routing.
- Finally, the policy map will be mapped into the inbound direction of the appropriate layer 3 interface.
Conclusion
This document is just like a drop from a glass of water. There are variety of situations were the policy based routing can be used.

