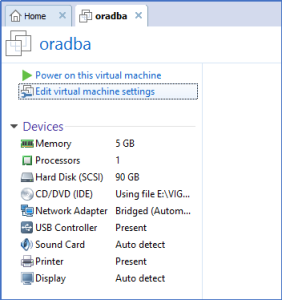
Description:
Already we have created partition while installed the operating system. But after installation, we need a new one partition means we have to do some configuration in it. So through this topic you get steps of create new one partition. Do the following steps one by one.
Let us create a new partition in Linux, start the virtual machine (VM)
Step 1: Shutdown the machine and click on edit virtual machine settings.
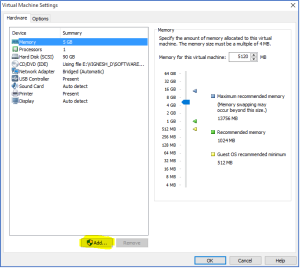
Step 2: Click on Add option in the bottom of the image and click OK.
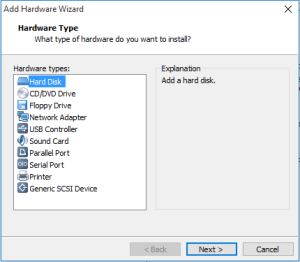
Step 3: Click on Hard Disk into the Hardware types and click next.
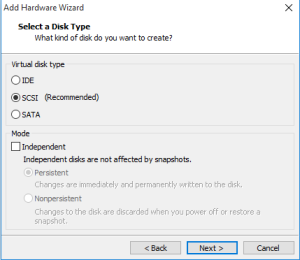
Step 4: Select SCSI (recommended) and click next and if you need immediate changes then click on persistent.
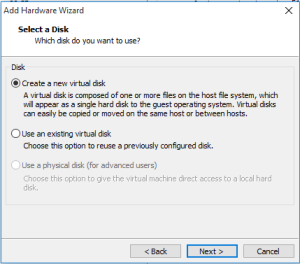
Step 5: Select create a new virtual disk.
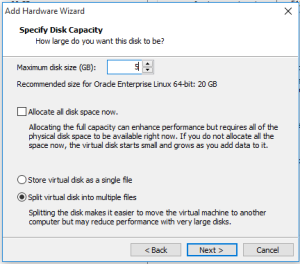
Step 6: Specify the Disk Capacity in the given box.
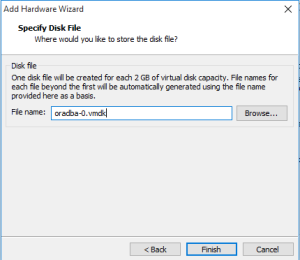
Step 7: Specify Disk file that where you would like to store this disk file.
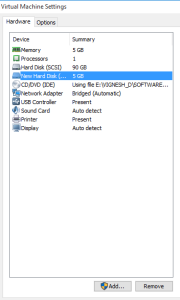
Step 8: The allocated size will be added in the hardware and go to Linux command line.
Step 9: To list the information about block devices. In the list of block devices, you get the new disk partition.
[oracle@xavier ~]$ lsblk -o NAME,SIZE,MOUNTPOINT
NAME SIZE MOUNTPOINT
sdb 45G
└─sdb1 45G
sr0 4.4G /run/media/oracle/OL-7.7 Server.x86_64
sda 40G
├─sda2 39G
│ ├─ol-swap 3.9 [SWAP
│ └─ol-root 35.1G /
└─sda1 1G /boot
Step 10: Login as a root user.
[oracle@oradba ~]$ su root
Password:
[root@oradba oracle]#
Step 11: To check the disk space
[root@oradba oracle]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /dev
tmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.3G 10M 2.3G 1% /run
tmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/ol-root 35G 9.6G 26G 28% /
/dev/sda1 5.0G 227M 4.8G 5% /boot
/dev/mapper/ol-u01 40G 25G 16G 62% /u01
tmpfs 467M 4.0K 467M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 467M 28K 467M 1% /run/user/1000
Step 12: To create a new partition, we have to mention the disk name in the fdisk command.
- Give the below command for display the file system that we have allocated.
[root@oradba oracle]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 96.6 GB, 96636764160 bytes, 188743680 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000e682c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 10487807 5242880 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 10487808 178276351 83894272 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/sdb: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/ol-root: 37.6 GB, 37580963840 bytes, 73400320 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/ol-swap: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/ol-u01: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Step 13: To invoke it, run the below command with the allocated file system.
[root@oradba oracle]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x0643df6c.
To create a new partition, then enter the option ‘n’
Command (m for help): n
To create another primary partition, then enter the open ’p’
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Enter the default given below
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-10485759, default 2048): 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-10485759, default 10485759):
Using default value 10485759
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 5 GiB is set
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
Now, the new partition has been created successfully.
To force the Kernel to reload the partition table, run the command below
[root@oradba oracle]# partprobe
Step 14: To view the new partition, run the command below
[root@oradba oracle]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb
Disk /dev/sdb: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0643df6c
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 10485759 5241856 83 Linux
Step 15: mkfs – make file system
- It uses for make a file system on a storage.
- Run the below command to format the /dev/sdb partition in ext4 file system.
[root@oradba oracle]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
327680 inodes, 1310720 blocks
65536 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1342177280
40 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
[root@oradba oracle]# cd
To view the new partition, use the command lsblk fdisk -l /dev/sdb1
Step 16: Make a directory in the root location to assign the disk name
[root@oradba ~]# mkdir /backup
Step 17: To mount the disk, run the command below
If you need, you can change the ownership using chown.
[root@oradba ~]#chown oracle:oinstall /backup
[root@oradba ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /backup
Step 18: List the disk usig df -h. It will be shown the new partition disk
[root@oradba ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /dev
tmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.3G 10M 2.3G 1% /run
tmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/ol-root 35G 9.6G 26G 28% /
/dev/sda1 5.0G 227M 4.8G 5% /boot
/dev/mapper/ol-u01 40G 25G 16G 62% /u01
tmpfs 467M 4.0K 467M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 467M 28K 467M 1% /run/user/1000
/dev/sdb1 4.8G 20M 4.6G 1% /backup
Step 19: While we shutdown the virtual machine, the operation system will only read the volume and partition information from the fstab file.
- So we have to add entry of the new partition details in fstab.
- Open the fstab file and add using Vi editor command, after that only the partition name will display in the command of df -h, other wise it will be invisible whenever start the operation system.
[root@oradba ~]# cd /etc
[root@oradba etc]# ls -lrth fstab
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 541 Jul 29 12:40 fstab
[root@oradba etc]# vi fstab
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Fri Jul 29 12:40:19 2022
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under ‘/dev/disk’
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/ol-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=a8be8196-cd1b-40c6-899a-e97b69810bca /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/ol-u01 /u01 xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/ol-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb1 /backup ext4 defaults 0 0
[root@oradba etc]#
- Run lsblk -l command whether the disk has mounted or not.
Step 20: Shutdown the operating system then start the VM machine and login with root user.
[root@oradba etc]# init 0
- Once shutdown and startup the operating system,the mount point will be updated.
[oracle@oradba ~]$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /dev
tmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.3G 10M 2.3G 1% /run
tmpfs 2.3G 0 2.3G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/ol-root 35G 9.6G 26G 28% /
/dev/sda1 5.0G 227M 4.8G 5% /boot
/dev/sdb1 4.8G 20M 4.6G 1% /backup
/dev/mapper/ol-u01 40G 25G 16G 62% /u01
tmpfs 467M 4.0K 467M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 467M 28K 467M 1% /run/user/1000
- It’s created successfully. Now you are able to access the new disk.