Query Store
- The Query Storeis a feature in SQL Server that helps you monitor query performance by capturing a history of queries, plans, and runtime statistics, etc.
Benefits of using the Query Store
- You can get information on SQL Server query plan selection and performance with the Query Store feature.
- The Query Store quickly finds performance differences caused by query plan changes, which simplifies performance troubleshooting.
- Plans, runtime statistics, and query histories are automatically recorded by Query Store and are saved for further review.
- It divides data into time frames so you may observe usages in database and can able to understand when server query plan modifications occurred.
Information in the Query Store
- Query Store collects plans for DML Statements such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, MERGE, and BULK INSERT.
- Query Store does not collect plans for DDL statements such as CREATE INDEX, etc.
- The Query Store could reveal the SELECT and INSERT commands used internally to add data to a new index.
Enable the Query Store Using SQL Server Management Studio
- Note: Requires at least version 16 of Management Studio.
- In Object Explorer, right-click a database, and then select Properties.
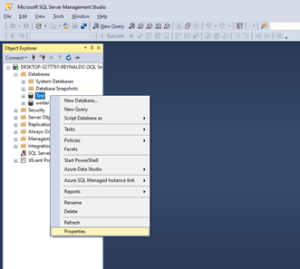
- In the Database Properties dialog box, select the Query Store page.
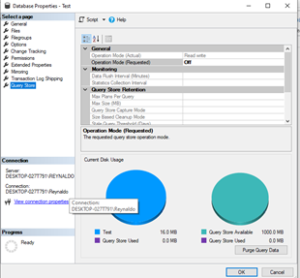
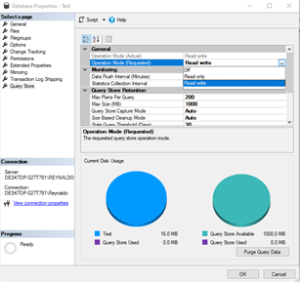
- In the Operation Mode (Requested) box, select Read Write.
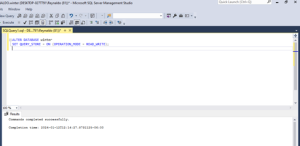
Enable the Query Store Using Transact-SQL statements
ALTER DATABASE statement to enable the query store for a given database.
ALTER DATABASE <database_name>
SET QUERY_STORE = ON (OPERATION_MODE = READ_WRITE);
Recent Posts
