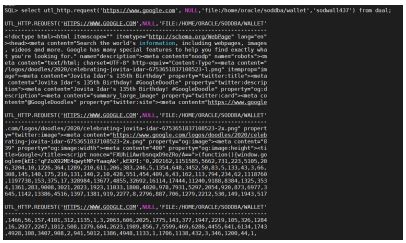
How to access HTTPS/SSL URL via utl_http using the orapki wallet command
Goal:
Our goal is to call/access the HTTPS/SSL url from within PL/SQL
The instruction provided here should also work for accessing other secure websites using PL/SQL as long as you have loaded the valid certificates into wallet.
Example: Here I am calling a google website
Steps to be followed,
- Get the certificates
- Create a wallet and Add certificates to wallet
- Create an ACL
- Connect to HTTPS
Step 1: Get the certificates
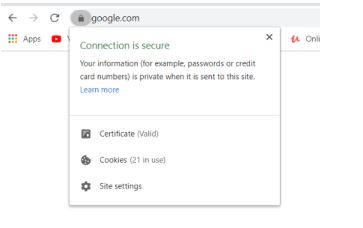
Go to the website in a web browser https://www.google.com
Click on the padlock symbol and then Certificate
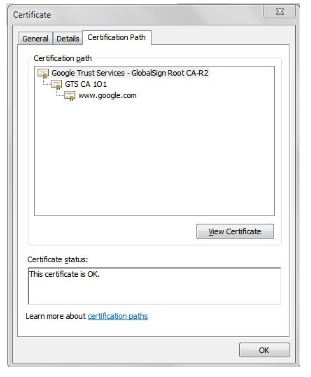
Now go to Certification Path and click on View Certificate
Note:
The top two certificate must be downloaded separately one after another as a separate certificates file. Do not download the last leaf [www.google.com]
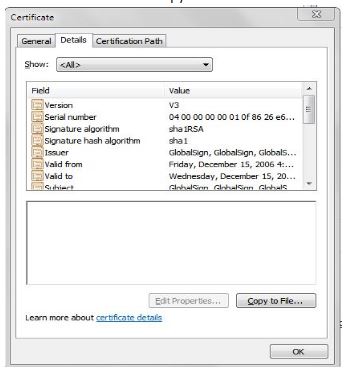
And then now click on Copy to File
A wizard will open, in that click Next button
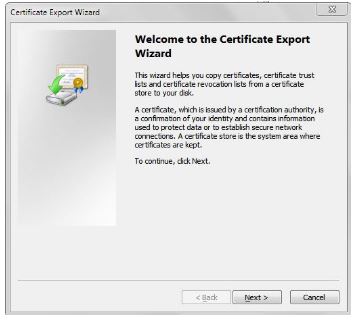
Choose Base-64 encoded X.509 (.CER) option
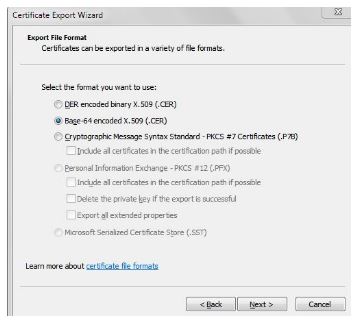
Specify a file name to save the certificate
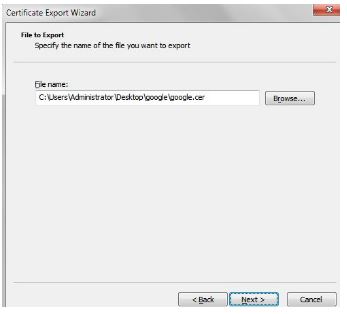
Click Next and then Finish
Now the Certificate is exported successfully

Similarly download the second certificate from the above chain in Certification path
Step 2 : Create a Wallet and Add certificates to Wallet
What is Wallet?
This Wallet is nothing but a container, secured with password, which stores certificates needed to setup the secured socket connection.
You can create a wallet and add certificate to Wallet using below command
mkdir -p /home/oracle/soddba/wallet
chmod -R 777 /home/oracle/soddba/wallet
orapki wallet create -wallet /home/oracle/soddba/wallet -pwd Orasod437 -auto_login
orapki wallet add -wallet /home/oracle/soddba/wallet -trusted_cert -cert “/home/oracle/soddba/wallet/google.cer” -pwd Orasod437
orapki wallet add -wallet /home/oracle/soddba/wallet -trusted_cert -cert “/home/oracle/soddba/wallet/google1.cer” -pwd Orasod437
Step 3: Create an ACL
Following is the command to create an ACL for the user. By doing this the’ XXUAC’ user will be able to access this URL
Assign the following ACL privilege to the user(In my case user is ‘XXUAC’) by logging as sysdba
conn / as sysdba
begin
dbms_network_acl_admin.create_acl (
acl => ‘utl_http1.xml’,
description => ‘HTTP Access’,
principal => ‘XXUAC’,
is_grant => TRUE,
privilege => ‘connect’,
start_date => null,
end_date => null
);
dbms_network_acl_admin.add_privilege (
acl => ‘utl_http1.xml’,
principal => ‘XXUAC’,
is_grant => TRUE,
privilege => ‘resolve’,
start_date => null,
end_date => null
);
dbms_network_acl_admin.assign_acl (
acl => ‘utl_http1.xml’,
host => ‘*’,
lower_port => NULL,
upper_port => NULL
);
commit;
end;
/
Step 4: Connect to HTTPS
Now create a procedure as below, before accessing the URL
Conn XXUAC/xxxxxxxx
Create the following procedure
DECLARE
lo_req UTL_HTTP.req;
lo_resp UTL_HTTP.resp;
BEGIN
UTL_HTTP.SET_WALLET (‘file:/home/oracle/soddba/wallet’,’Orasod437′);
lo_req := UTL_HTTP.begin_request(‘https://www.google.com/’);
lo_resp := UTL_HTTP.get_response(lo_req);
dbms_output.put_line(lo_resp.status_code);
UTL_HTTP.end_response(lo_resp);
END;
/
Now make a HTTPS call from within PL/SQL,
select utl_http.request(‘https://www.google.com’, NULL,’file:/home/oracle/soddba/wallet’, ‘Orasod437’) from dual;