Introduction:
This blog explains about the feature of dynamic routing protocol in a Network.
Why Dynamic routing protocol?
During the early days of the network, static routing was in the play. But later at the stage when the network start to grow static routing were being a problem such as configuration overhead, Layer 3 routing loops, unable to perform load balancing/sharing, auto redundancy etc.
Here is where the dynamic routing protocols came into. There are many types of dynamic routing protocols.
These protocols were able to learn networks automatically and built the routing table, were able to do load balancing and use multiple links across the routers more effectively. Also, any changes in the topology triggers to update the routing table automatically.
We will see a simple scenario here were the auto failover and load balancing is achieved. We will be using EIGRP (Enhanced Interior gateway routing protocol. It’s a Cisco proprietary dynamic routing protocol)
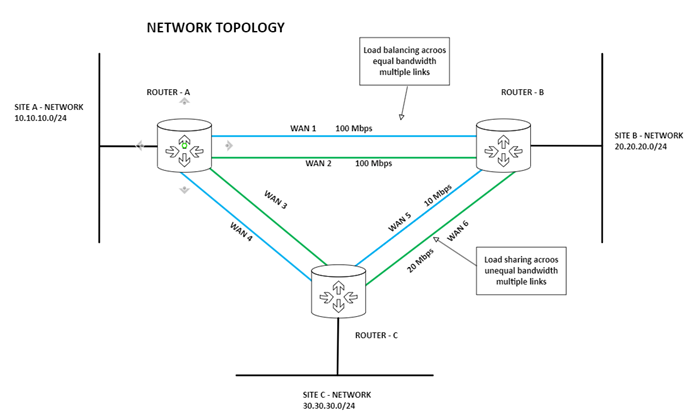
Step-by-Step Explanation:
In the following sections I will walt thru on the various faults on these topologies and explain how dynamic routing protocol helps to achieve high availability and auto failover.
Event number 1: What happens if WAN Link 1 goes down?
Answer: The WAN link 2 will handle the traffic between site A and Site B. But with a reduced bandwidth from 200 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
Event number 2: What happens if both WAN Link 1 & 2 goes down?
Answer: No worries, the traffic between Site A and Site B will pass thru the Site C. But there will be some additional time/latency and of course not impacting the business.
Conclusion
In today’s advance technologies like Software defined networks, SD-WANs, Cloud environments it may look most of the dynamic routing protocols has peeled and not used widely. But that’s not the true. Almost all dynamic routing protocols are used in the underlaying bare metals and used as underlaying protocols.
