In this post let us understand the Oracle dataguard Architecture and processes with the help of diagrams.
Oracle Dataguard Architecture: how data flows when standby is configured
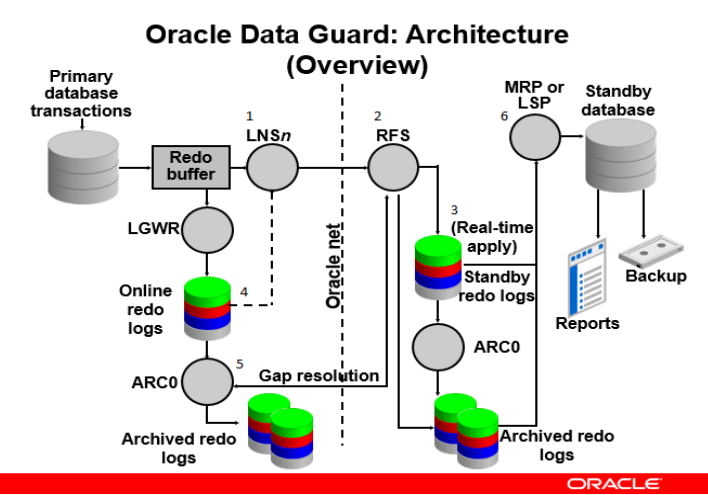
- LNS process of primary database captures redo from redo log buffer.
- Send it to RFS process of standby database through oracle net.
- RFS process then writes that redo information to standby redo log files.
- If LNS process is not fast enough to capture redo information before it goes to online redo log files or if redo data are going online redo log files very quickly then LNS process will read from Online redo log files and send redo to RFS process through Oracle net.
- If some network outage occur and online redo log gets log switch and data goes to archived redo log files , before its been written to standby redo log files then RFS process will directly communicate to ARCn process and works for Archive log gap resolution.
- Once with any possible way redo are written to standby redo log files then , MRP [in case of physical dataguard] or LSP [in case of logical dataguard] process apply that redo or sql to standby database.
- The fetch archive log (FAL) client is the MRP process. The fetch archive log (FAL) server is a foreground process that runs on the primary database and services the fetch archive log requests coming from the FAL client. A separate FAL server is created for each incoming FAL client. FAL_SERVER specifies the FAL (fetch archive log) server for a standby database. The value is an Oracle Net service name, which is assumed to be configured properly on the standby database system to point to the desired FAL server.
FAL_CLIENT and FAL_SERVER parameters are useful as the managed-recovery process in the physical database will automatically check and resolve gaps at the time redo is applied. This helps in the sense that you don’t need to perform the transfer of those gaps by yourself.
FAL_CLIENT and FAL_SERVER only need to be defined in the initialization parameter file for the standby database(s). It is possible; however, to define these two parameters in the initialization parameter for the primary database server to ease the amount of work that would need to be performed if the primary database were required to transition its role.
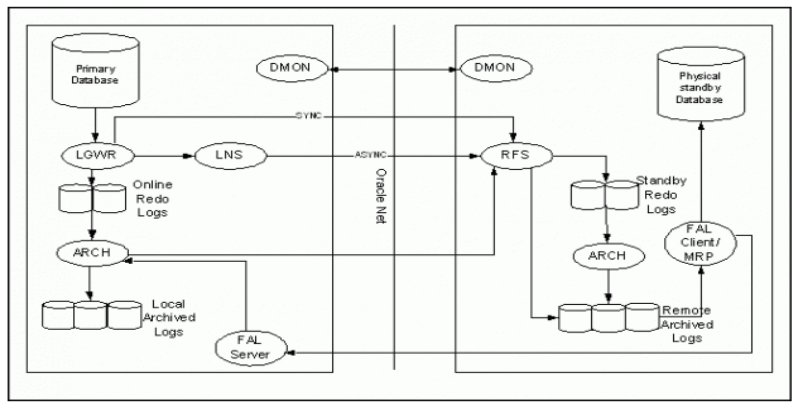
PRIMARY DATABASE PROCESSES AND STANDBY DATABASE PROCESSES
PRIMARY DATABASE PROCESSES
1. LGWR: LGWR collects transaction redo information and updates online redo log files.
2. How redo data is send
REDO data is send either through ARCn process or LGWR process.
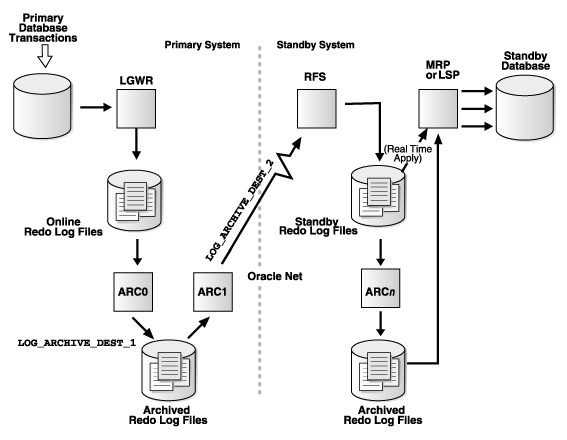
Using ARCn process
This is default and supports only maximum performance. log_archive_max_processes init parameter specifies the max number of ARC process to be invoked when primary db is started. Default value is 4 and it is dynamic parameter can be adjusted with ALTER SYSTEM
On primary database, after ARC0 successfully archives online redo logfile to local destination, the ARC1 process transmits redo from local destination to the remote standby destination. On standby database, RFS process will write redo data to archived redo logfiles.
Using LNS process [Log writer network server]: LNS process works in two way.
SYNC mode : When you have configured your dataguard environment in sync Redo transport Service , LGWR passes redo to LNS process , which transfers data directly to RFS process on the standby database. LGWR waits for confirmation from the LNS process and LNS process waits confirmation from RFS process that redo data are applied to standby database before acknowledging commit.
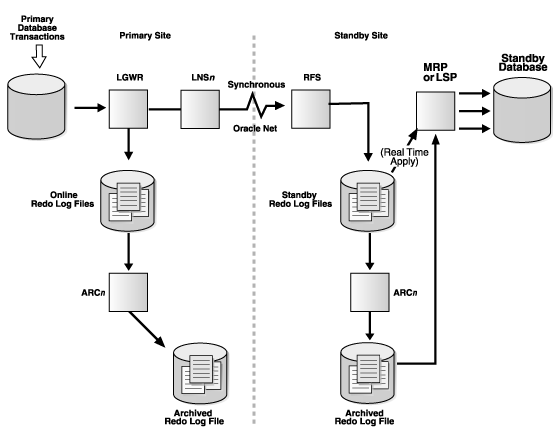
ASYNC : When you have configured async redo transport service, it is independent of LNS process , whether LNS process have read from redo log buffer or from online redo log files . Dataguard just starts asynchronous LNS process , other than that LGWR has no interaction with any asynchronous standby destinations. In simple terms , data guard will not wait for any acknowledgement from standby database that redo are applied or not and keeps on doing its work. So it is way faster than sync mode .
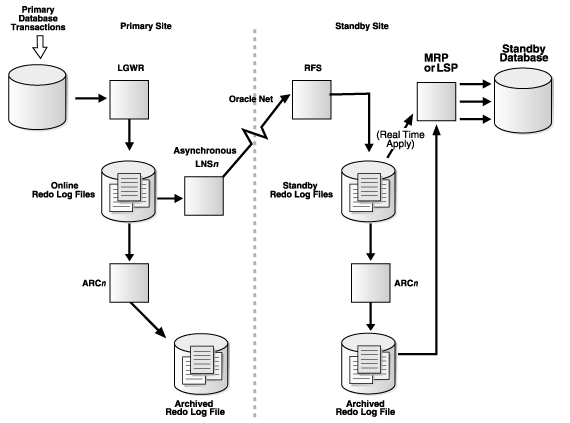
- ARCn Process : As we know ARCn process creates a copy of the online redo log files . ARCn is also responsible for shipping redo data to an RFS process at a standby database and for pro-actively detecting and resolving gaps on all standby database.
STANDBY DATABASE PROCESSES
- RFS [Remote File Server]: As we have seen above RFS process can get redo data either from LNS process or from ARCn process of primary and RFS process can writes redo information to standby redo logs files.Each LNS and ARCn process that communicates with Standby database has its own RFS process.
- ARCn [Archiver]: The ARCn process archives standby redo logs.
- MRP [Managed Recovery Process]: In case of physical dataguard MRP process comes into play.MRP process applies archived redo log information to the physical standby database.You can start managed recovery using “ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE” this foreground session performs recovery. And if you want to perform recovery on background then you can optionally use DISCONNECT FROM SESSION. clause where MRP background process will start .
- LSP [Logical Standby ]:It comes into play for logical dataguard only. It controls the application of archived redo log information to the logical standby database. LSP process will transform redo data into sql statements and then these sql statements will be applied to logical standby database.
In the next article, we see about DATAGUARD PROTECTION MODES
