Introduction:
SQL Server Linked Servers is a feature in Microsoft SQL Server that allows you to connect and execute commands against OLE DB data sources on different servers. This functionality enables seamless interaction with external databases or other SQL Server instances as if they were part of the local server. Linked Servers are particularly useful in scenarios where data from multiple sources need to be integrated, queried, or managed collectively without needing to replicate data between systems. This feature supports various data sources, including Oracle, MySQL, Excel, and other SQL Server instances, making it a versatile tool for enterprise-level data management and integration.
| Server | DESKTOP-QBAKU2I\DIS |
| Sever to be linked | DESKTOP-QBAKU2I |
| Common login | vijay |
First create a common login in both servers for linking purpose. Using a separate login for linking purpose is advisable.
Step 1: In this scenario we are creating same login for linking purpose.
Server: DESKTOP-QBAKU2I\DIS
Server: DESKTOP-QBAKU2I
Step 2: Create a new linked server in DESKTOP-QBAKU2I\DIS
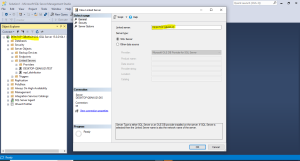
Step 3: Provide the remote login (user login) that we have created on the server DESKTOP-QBAKU2I.
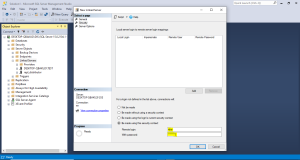
Step 4: After successful creation of linked server. Now it is possible to access the data’s of DESKTOP-QBAKU2I sever in DESKTOP-QBAKU2I\DIS.
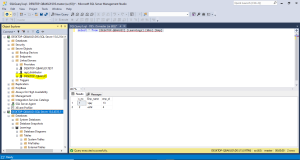
Conclusion:
SQL Server Linked Servers offer a powerful means of integrating and managing data across diverse platforms. By providing the ability to query and manipulate remote data sources directly, they enhance the capabilities of SQL Server, enabling more efficient and centralized data operations. However, it’s essential to implement Linked Servers with proper security and performance considerations to avoid potential pitfalls. When used effectively, Linked Servers can significantly streamline data workflows and enhance the overall functionality of SQL Server in complex environments.
