Consolidation and cloud environments reduce cost but can expose sensitive application data to those without a true need-to-know.
Data from one country may be hosted in an entirely different country, but access to that data must be restricted based on regulations of the country to which the data belongs. Oracle Database Vault controls provide increased security for these environments by preventing database administrators from accessing the applications data. In addition, controls can be used to help block application bypass and enforce a trusted-path from the application tier to the application data.
Oracle Database Vault provides four distinct separation of duty controls for security administration:
- Day-to-day database administrator tasks using the default Oracle Database DBA role
- Security administrator tasks using the DV_OWNER and DV_ADMIN roles
- Account administrator tasks using the DV_ACCTMGR role
- Grants of roles and privileges by a named trusted user
Oracle Database Vault separation of duty controls can be customized, and organizations with limited resources can assign multiple Oracle Database Vault responsibilities to the same administrator, but using separate accounts for each separation-of-duty role to minimize damage to the database if any one account is stolen and leveraged.
Oracle customers today still have hundreds and even thousands of databases distributed throughout the enterprise and around the world. However, for database consolidation as a cost-saving strategy in the coming years to be effective, the physical security provided by the distributed database architecture must be available in the consolidated environment. Oracle Database Vault addresses the primary security concerns of database consolidation.
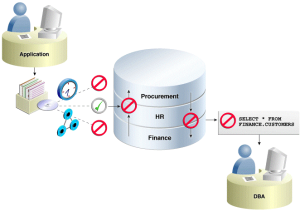
- Administrative privileged account access to application data: In this case, Oracle Database Vault prevents the database administrator from accessing the schemas that are protected by the Finance realm. Although the database administrator is the most powerful and trusted user, this administrator does not need access to application data residing within the database.
- Separation of duties for application data access: In this case, the HR realm owner, created in Oracle Database Vault, has access to the HR realm schemas. The following figure shows how Oracle Database Vault addresses the following database security concerns:
Database consolidation can result in multiple powerful user accounts residing in a single database. This means that in addition to the overall database administrator, individual application schema owners also may have powerful privileges. Revoking some privileges may adversely affect existing applications. Using Oracle Database Vault realms, you can enforce access to applications through a trusted path, preventing database users who have not been specifically authorized access from using powerful privileges to look at other application data. For example, a database administrator who has the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege can be prevented from using that privilege to view other application data residing in the same database.
Data needs Role-based access to improve securing data. It is important to ensuring those feature to limit the user. By using the feature of SYSBACKUP, SYSDG and SYSKM will do this job. Use the feature of Oracle Vault to ensure these.
