DBA Auditing:
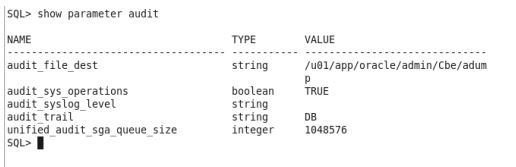
It is used to audit all the operations performed by the user on schema objects, gor this we need to enable auditing for a database, to enable it we have to set audit_sys_operations to TRUE and also have to set the audit_file_dest destination where the audit files should be saved, I have enabled auditing for my current database
STATEMENT LEVEL:
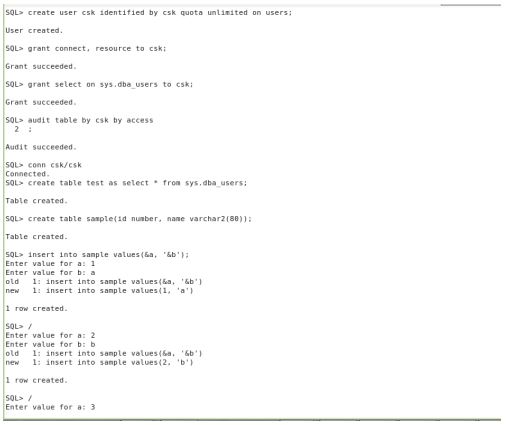
I have created a user and enabled the auditing for that user to audit all the schema object operations and I am going to audit all the dml and ddl operations that are going to be performed in the schema object, in statement level, we can see what kind of statement can be audited in the view called DBA_STMT_AUDIT_OPTS
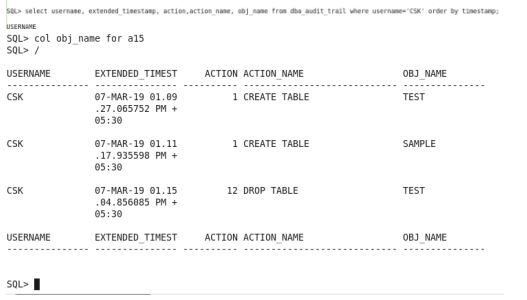
We can see what kind of operations are performed in schema object in the view called DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL
OBJECT LEVEL:
In object level we can enable auditing for objects like tables, indexes, synonyms, segments and dml operations in the schema objects, things that we are going to audit can be seen in the view called
DBA_OBJ_AUDIT_OPTS
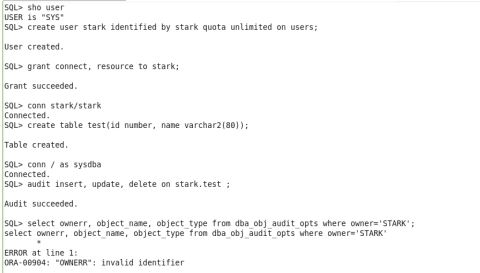
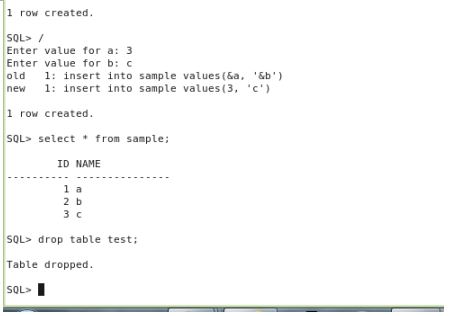
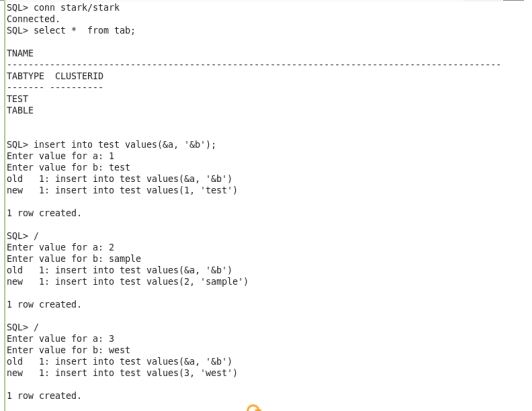
I performed auditing on the table with dml operations and also inserted ,update some records and deleted a record in object level we can not audit the ddl statements in the object level


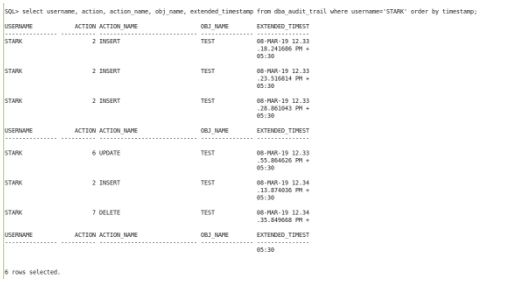
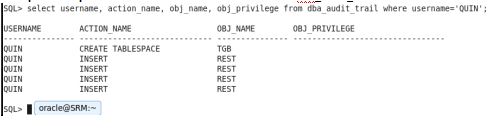
When I viewed the dba_audit_trail view I got the information of the dml operations performed by the user on the schema object
PRIVILEGE LEVEL:
In privilege level only the privileges allocated to the users can only by audited, this will audit all the privileges that the user has to that particular schema object, this can be viewed by dba_priv_audit_opts view
I audited the create tablespace privilege of the user by granting the tablespace privilege to the user
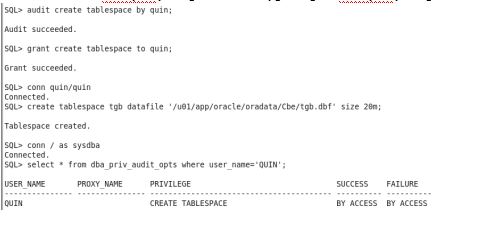
The operations performed in the user can be viewed in the dba_audit_trail view
Posted by :Sakthi Sethu Perumal S
