How to Configure Peer-to-Peer Replication in SQL Server: Complete Guide
Introduction:
In high-availability environments, applications often require data to be available for both read and write operations across multiple servers. A common issue faced is handling heavy read/write workloads on a single database server, which can lead to performance bottlenecks and downtime risks.
This blog explains how Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Replication in SQL Server helps distribute data across multiple servers while allowing read and write access.
Why we need to do:
In many real-time systems, a single primary database handles all user transactions. As user traffic grows, this can cause:
Causes of the issue:
- High read and write load on one server.
- Performance degradation during peak usage.
- Limited scalability with a single database instance.
- Need for high availability without changing application logic.
Impact of the issue:
- Slow application response time.
- Increased risk of downtime.
- Difficulty in scaling the database horizontally.
- User experience degradation.
Peer-to-Peer Replication addresses these issues by allowing multiple database servers to act as equals, distributing the workload efficiently.
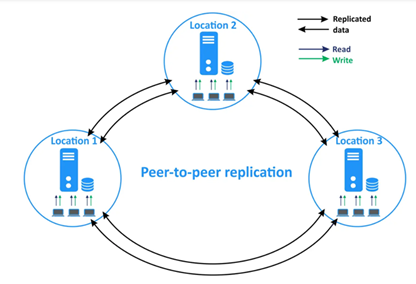
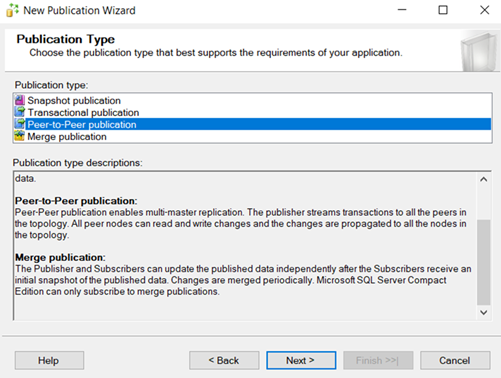
PEER TO PEER Replication
Peer to peer replication works DB Level. In peer-to-peer replication there is no snapshot option is not available.
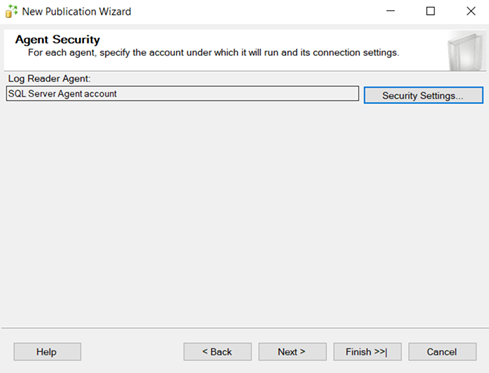
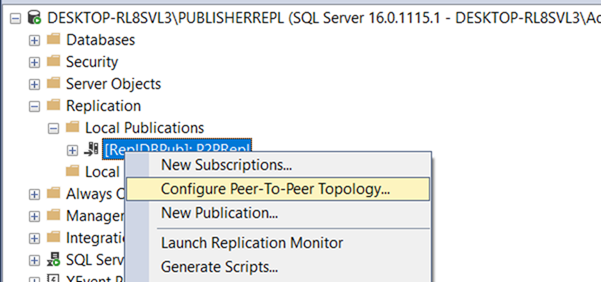
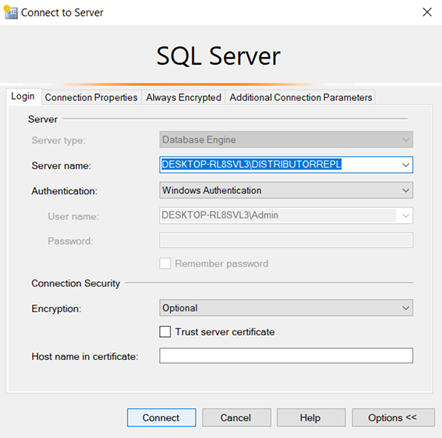
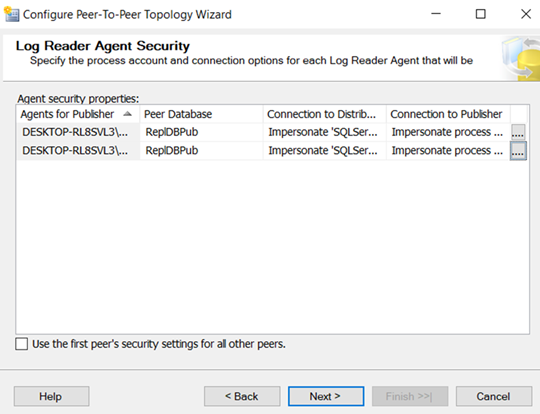
–Configure all three machines as distributor.
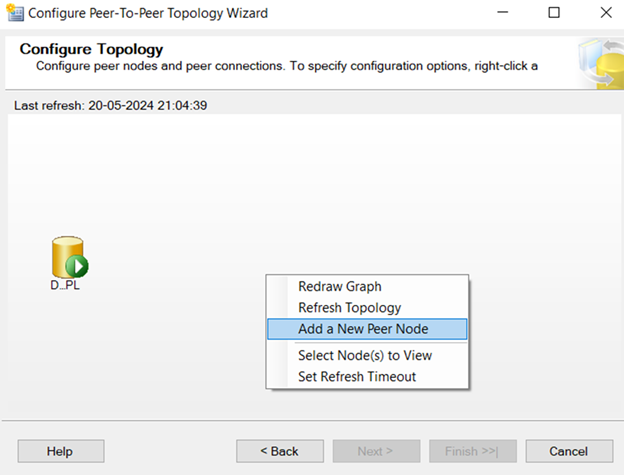
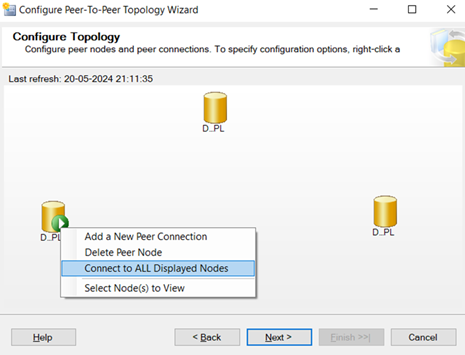
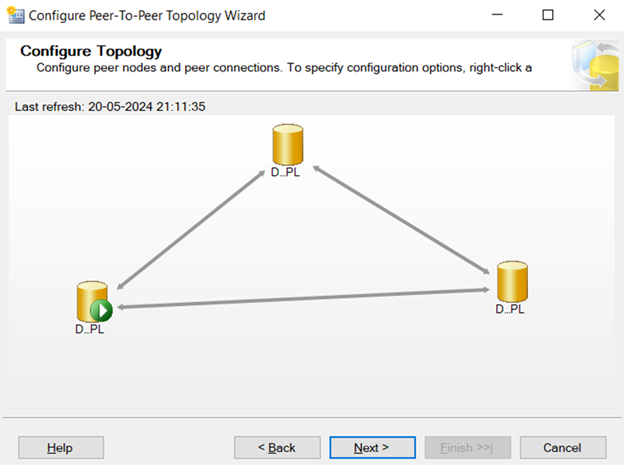
–In peer to peer every node is called as Peer.
–Where ever you insert the data in one peer it goes to another peers also.
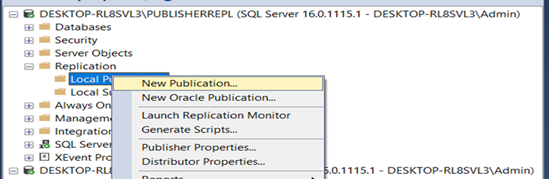
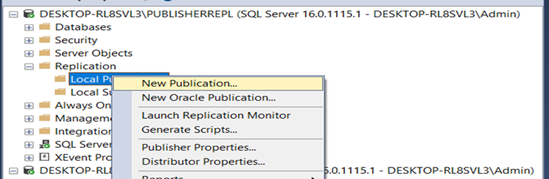
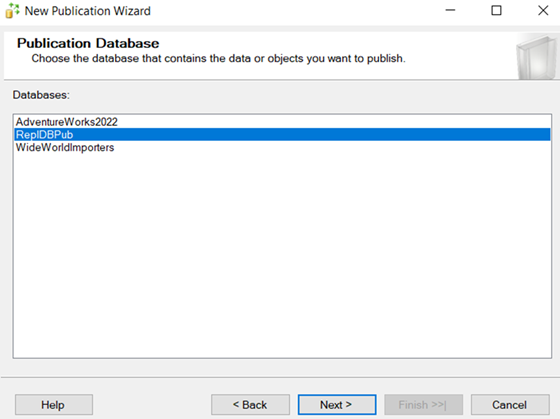
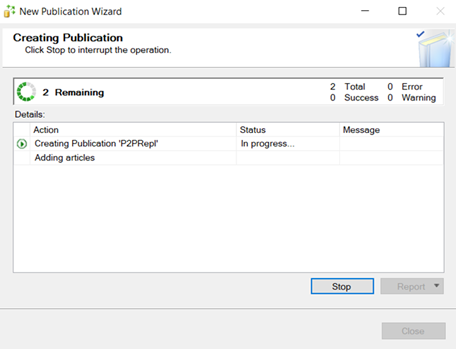
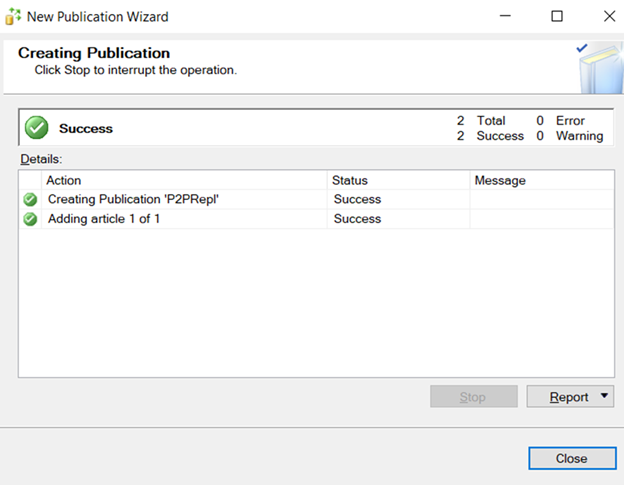
–Go to one of the machines.
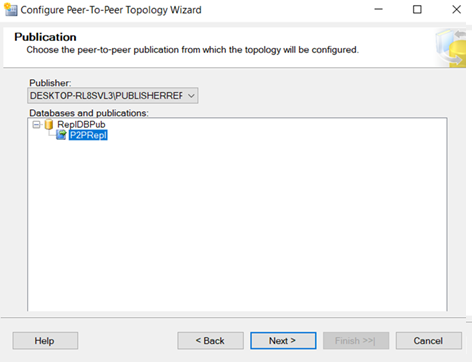
After configuring all the machines as publisher. Go to any one of the machines
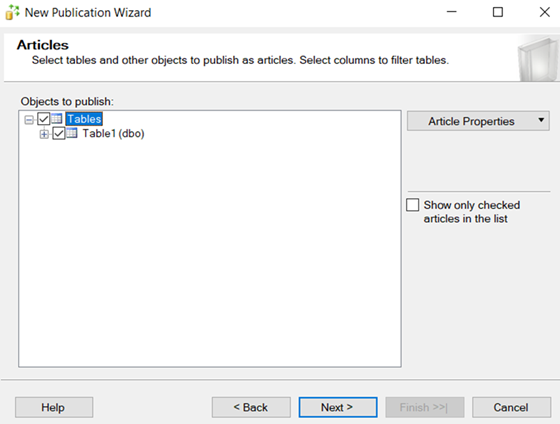
–every table must have primary key.
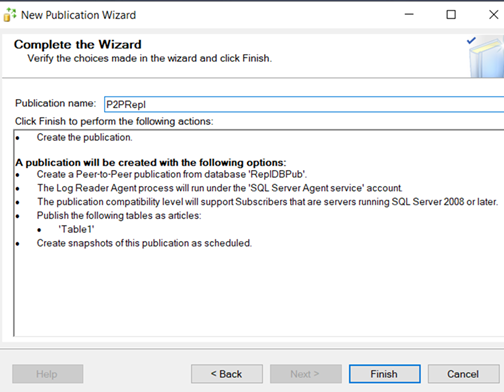
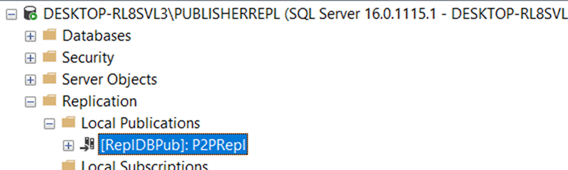
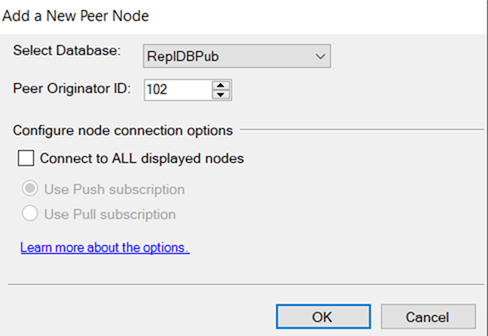
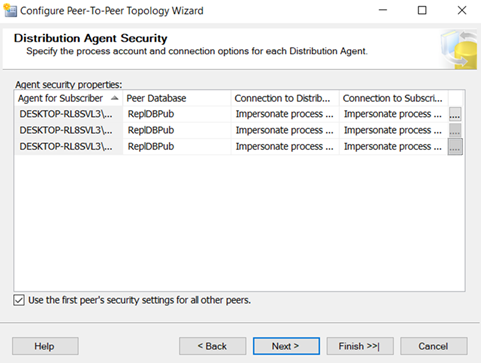
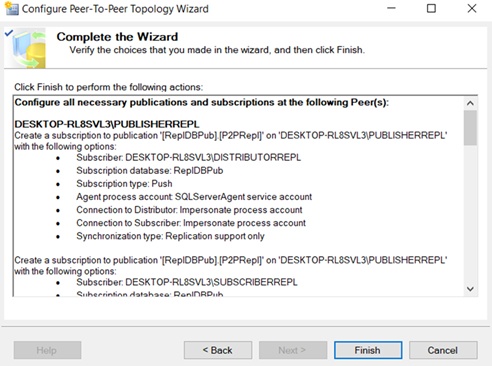
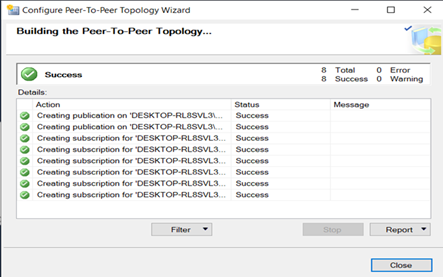
Add Publisher, Distributor and subscriber.
In this Replication, all three nodes are publisher, Distributor and subscriber. All three are inter linked.
Conclusion:
Peer-to-Peer Replication is an effective solution for scaling out SQL Server databases and improving availability. By distributing workload across multiple peers, it reduces performance bottlenecks and enhances system resilience.
When implemented with proper application design to avoid conflicts, Peer-to-Peer Replication provides a powerful and scalable replication strategy for high-traffic environments.