Introduction:
Running large language models (LLMs) locally is a great way to develop private, low-latency applications without depending on cloud APIs. However, beginners often run into installation and resource issues when trying to run LLMs on their machines.
Why we need to do / Cause of the issue:
Most Large Language Models are commonly accessed through public cloud APIs. While this approach is convenient, it comes with several limitations. Public APIs often require a constant internet connection, involve usage costs based on requests or tokens, and may introduce latency depending on network conditions. Additionally, sending sensitive or internal data to third-party servers can raise privacy and security concerns. These challenges make public APIs less suitable for learning, experimentation, offline development, or applications that require full control over data. Running LLMs locally helps overcome these issues by providing better privacy, lower long-term cost, offline access, and greater flexibility for developers.
How do we solve:
Follow these steps to install and run an LLM locally, then use it from a Python project.
1.Install ollama
Ollama is a tool that makes it easy to install and run LLMs locally.
Head to https://ollama.com/ and install ollama as per your specifications.
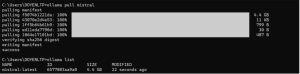
2. Pull a model
Browse the Ollama model library at https://ollama.com/library , choose a chat-capable model, then pull it locally:
Open command prompt and run below command to install the model.[Text Wrapping Break]ollama pull <model_name>
3. Test the model from the command line
Now you have a LLM in your local machine to play around!
You can use your local LLM in your python projects.
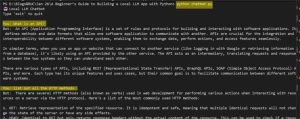
4. Use your local LLM in a Python project
Now you have an LLM running on your local machine, you can start using it in your Python applications.
Below is a simple Python chatbot that sends live user input to your local model. Replace MODEL_NAME with the model you pulled.
from ollama import chat MODEL_NAME = “mistral”
print(“🤖 Local LLM Chatbot”)
print(“Type ‘exit’ to quit\n”)
messages = []
while True:
user_input = input(“You: “)
if user_input.lower() in [“exit”, “quit”]:
print(“Goodbye 👋”)
break
messages.append({“role”: “user”, “content”: user_input})
response = chat(
model=MODEL_NAME,
messages=messages
)
bot_reply = response[“message”][“content”]
print(f“Bot: {bot_reply}\n“)
messages.append({“role”: “assistant”, “content”: bot_reply})
Test the implementation by running the Python file and interacting with the chatbot.
In addition to using the model directly, your local LLM can also be accessed through an API. This allows you to integrate the model with applications, services, or automation workflows, just like a cloud-based LLM, but running entirely on your local system.
Conclusion:
We have explored how to run a Large Language Model locally using Ollama and integrate it into a Python application, eliminating dependency on cloud services while improving privacy and control. By building a simple chatbot and interacting with the model through Python and APIs, we demonstrated how easily local LLMs can be used in real-world projects. This setup can be further enhanced by adding a user interface, database integration, conversation memory, or exposing the model through secure APIs, making it a strong foundation for scalable and customizable AI applications.
