Archiving and Deleting Data From SQL Server Database
Server: SERVER1
Main Database: DB1
Archive Database: DB1_archive
Target Table: dbo.PerformanceCounters
Objective:
To archive and delete data older than 90 days from dbo.PerformanceCounters in a batch-wise manner, store it in an archive database.
Pre-Checks:
- Confirm Data Availability for a particular table
USE DB1
GO
SELECT
MIN(SnapshotDate) AS [DataAvailableFrom],
MAX(SnapshotDate) AS [DataAvailableTo]
FROM dbo.PerformanceCounters;
- Check Row Count in Both Databases
— Run on both DB1 and DB1_archive
SELECT
s.name AS SchemaName,
t.name AS TableName,
SUM(p.rows) AS [RowCount]
FROM sys.tables t
JOIN sys.schemas s ON t.schema_id = s.schema_id
JOIN sys.partitions p ON t.object_id = p.object_id
WHERE p.index_id IN (0,1)
GROUP BY s.name, t.name
ORDER BY [RowCount] DESC;
- Check Rows Older Than 90 Days
USE DB1;
GO
SELECT COUNT(*) AS RemainingOldRows
FROM dbo.PerformanceCounters
WHERE SnapshotDate < DATEADD(DAY, -90, GETDATE());
—
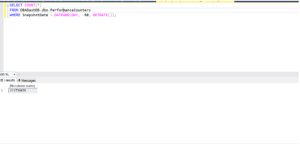
Archival Process (Batch-Wise)
Repeat this batch until no records are returned by the pre-check above.
USE DB1;
GO
WITH BatchToArchive AS (
SELECT TOP (5000000) *
FROM dbo.PerformanceCounters
WHERE SnapshotDate < DATEADD(DAY, -90, GETDATE())
ORDER BY SnapshotDate
)
INSERT INTO DB1_archive.dbo.PerformanceCounters
SELECT * FROM BatchToArchive;
—
Deletion Process (Batch-Wise)
Repeat until no rows remain to delete.
USE DB1;
GO
WITH BatchToDelete AS (
SELECT TOP (2500000) *
FROM dbo.PerformanceCounters
WHERE SnapshotDate < DATEADD(DAY, -90, GETDATE())
ORDER BY SnapshotDate
)
DELETE FROM BatchToDelete;
Post-Archival Validation:
- Verify Row Count in Archive DB
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM DB1_archive.dbo.PerformanceCounters;
- Check if Old Rows Exist in Main DB
SELECT COUNT(*) AS RemainingOldRows
FROM DB1.dbo.PerformanceCounters
WHERE SnapshotDate < DATEADD(DAY, -90, GETDATE());
- Check the Data file used and unused space
USE [DB1]; — Replace with your database
GO
SELECT
name AS [LogicalName],
size / 128.0 AS [TotalSizeMB],
size / 128.0 – CAST(FILEPROPERTY(name, ‘SpaceUsed’) AS INT) / 128.0 AS [UnusedSpaceMB],
physical_name AS [FilePath]
FROM sys.database_files
WHERE type_desc = ‘ROWS’;
Conclusion
Implementing a batch-wise archiving and deletion strategy for the dbo.PerformanceCounters table helps maintain optimal database performance while ensuring historical data is preserved for future reference. By moving data older than 90 days to an archive database, we reduce the size of the active table, improve query efficiency, and support long-term data retention policies.
This approach not only helps in managing growing data volumes but also minimizes the performance impact on the production environment. Regular maintenance using such archiving strategies is essential for keeping SQL Server databases clean, efficient, and scalable.
