Merge Replication in SQL-Server
Introduction:
Merge Replication in SQL Server is used in distributed environments where multiple databases need to work independently and later synchronize data.
This guide explains why Merge Replication is needed, how it works, common issues, and important considerations, with a simple demo overview.
Learn how to configure Merge Replication in SQL Server, understand its behavior, and avoid common pitfalls while working in real-time and offline environments.
Why Do We Need Merge Replication in SQL Server?
In many real-time applications such as:
-
Field service systems
-
Offline applications
-
Branch or multi-location deployments
Databases are not always connected to the central server. Each location may update data independently and later reconnect to synchronize changes.
In such cases, traditional replication methods are not sufficient. Therefore, Merge Replication in SQL Server is required.
Causes of Data Synchronization Issues:
Data synchronization problems usually occur because of the following reasons:
-
Databases are updated at multiple locations
-
Network connectivity is intermittent or unreliable
-
Transactional replication is not suitable
-
Offline data changes must be merged later
As a result, maintaining data consistency becomes challenging.
Impact of the Issue:
If proper replication is not implemented, it can lead to serious problems such as:
-
Data mismatch between servers
-
Conflicting updates on the same records
-
Manual data reconciliation
-
Application errors
-
Incorrect reporting and analytics
To overcome these challenges, Merge Replication plays a critical role.
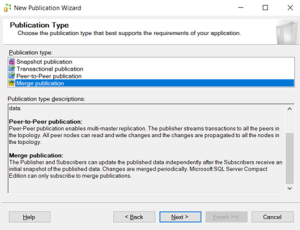
What Is Merge Replication in SQL Server?
Merge Replication allows both the Publisher and Subscriber to update data independently. Later, all changes are merged and synchronized.
-
Bidirectional replication
-
Publisher → Subscriber
-
Subscriber → Publisher
-
-
Suitable for offline and distributed environments
-
Conflict detection and resolution using a ranking system
-
Ideal for environments with intermittent connectivity
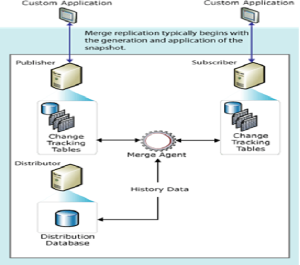
Merge Replication Architecture:
Agents Used
-
Merge Agent
-
There is only one agent used in Merge Replication
-
It handles data synchronization and conflict resolution
-
Primary Key Requirement.
-
Primary key is not compulsory
-
However, SQL Server automatically adds a uniqueidentifier column for tracking changes
Demo Overview – Merge Replication Configuration:
Prerequisites
-
Distributor configuration completed
-
Publication already created
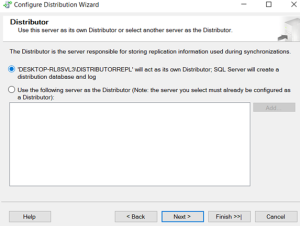
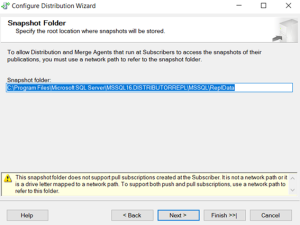
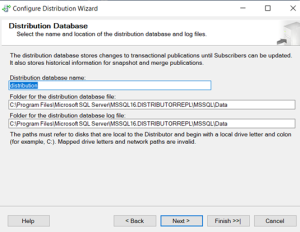
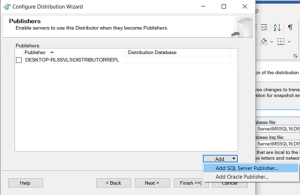
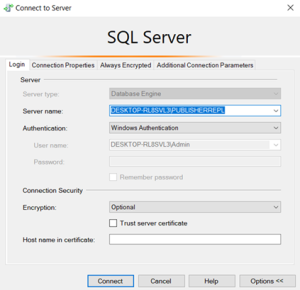
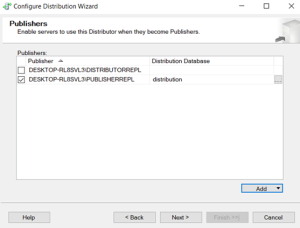
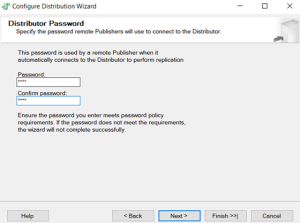
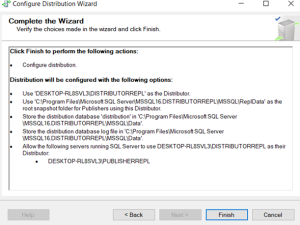
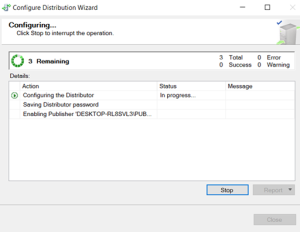
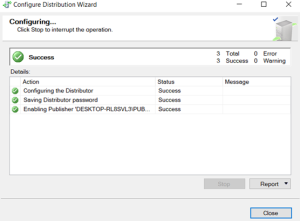
Distributor has been finished.
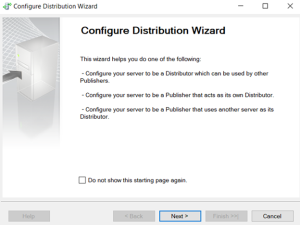
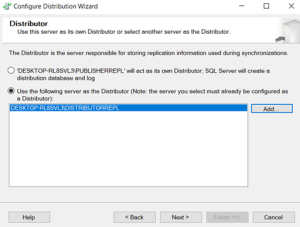
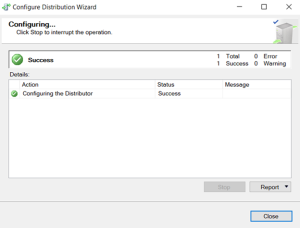
Publication configured.
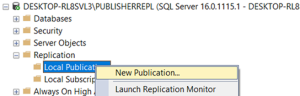
Now create local Publication.
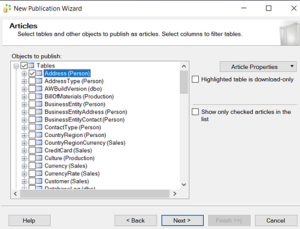
Create Local Publication
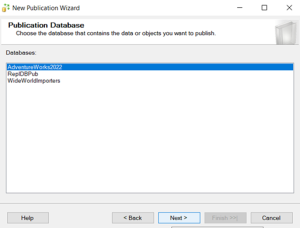
-
Configure a local publication
-
During configuration:
-
An extra column of type uniqueidentifier is added to tables
-
This increases table size
-
Snapshot generation time also increases
-
Important Note:
Sometimes INSERT statements may fail if developers are unaware of the newly added column.
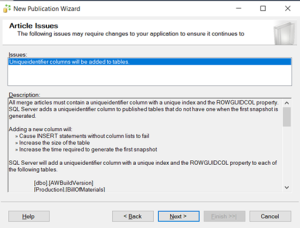
An Extra column will be added in the tables named as Unique identifier. By adding the new column table size will be increased.
-Insert statement will fail sometime because of developers don’t know new column is there.
-Snapshot time will be increased.
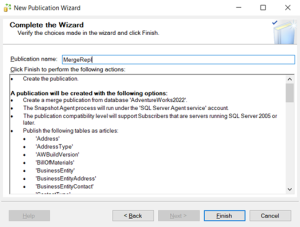
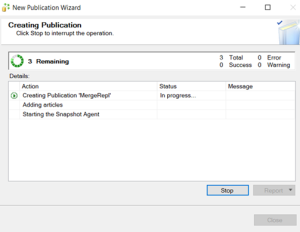
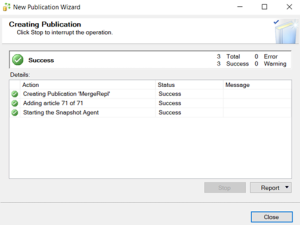
Publication has been completed.
Now Need to create local Subscription.
Create Local Subscription:
-
Configure the Subscriber
-
Synchronization is handled by the Merge Agent
-
Conflict resolution is managed using a ranking system, which decides the winning change
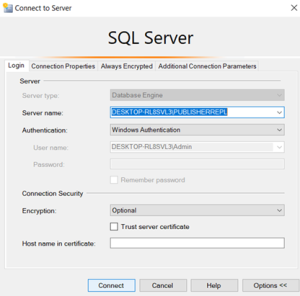
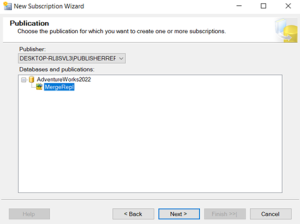
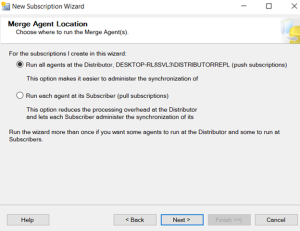
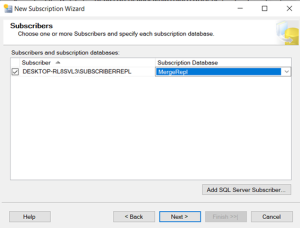
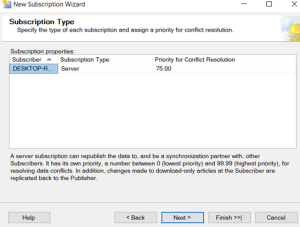
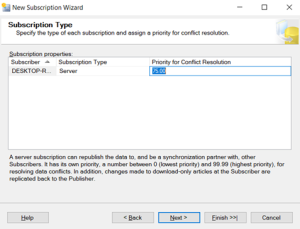
The Ranking system is used is too good.
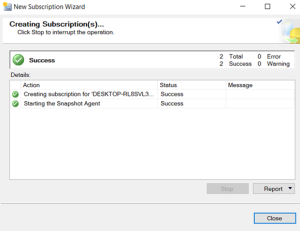
Conclusion:
Merge Replication in SQL Server is a powerful solution for synchronizing data across distributed and occasionally connected environments. It allows multiple databases to update data independently while ensuring consistency through intelligent conflict resolution.
With proper configuration, monitoring, and understanding of its behavior, Merge Replication helps organizations maintain reliable data synchronization for offline, real-time, and multi-location use cases.
