How to recover suspect/Recovery pending databases in SQL Server?
Introduction:
In SQL Server, a database may enter SUSPECT or RECOVERY PENDING state due to corruption, missing files, or insufficient resources.
What we need to do :
In SQL Server versions 2005 and later (including 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, 2019, and 2022), databases may enter a state called “Recovery Pending” or “Suspect”.
These states indicate that SQL Server is unable to bring the database online, usually due to issues like:
- Corrupted or missing database files
- Insufficient system resources (e.g., memory or disk space)
- Interrupted recovery process
Step-by-Step Recovery Process
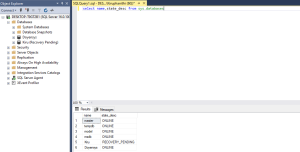
Use the below Query to check the status of all the databases.
- select name,state_desc from sys.databases
This will list the current status (e.g., ONLINE, RECOVERY_PENDING, SUSPECT) for each database.
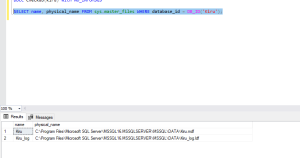
Verify File Paths
Check the physical file paths for the affected database:
- SELECT name, physical_name FROM sys.master_files WHERE database_id = DB_ID(‘Kiru’);
Make sure all paths are valid and files exist in the expected locations. If files are missing or moved, restore or remap them accordingly.
Restore missing files or remap them if they’ve been moved.
The below query shows what exactly is the issue for the database being recovery/suspect.
Run a consistency check to identify corruption or other problems:
- DBCC Checkdb(kiru) with NO_INFOMSGS
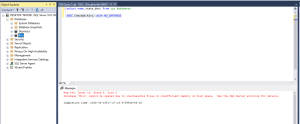
The error message we are getting it, Msg 945, Level 14, State 2, Line 3Database ‘Kiru’ cannot be opened due to inaccessible files or insufficient memory or disk space. See the SQL Server errorlog for details.
Review SQL Server Error Logs
Check the SQL Server error logs for detailed messages that explain why the database can’t be accessed. This will help determine the appropriate recovery action.
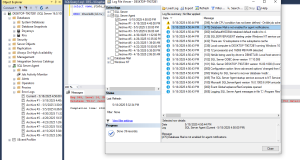
Verify Backup Availability
Confirm that a valid backup of the affected database exists and is stored in a reliable location.
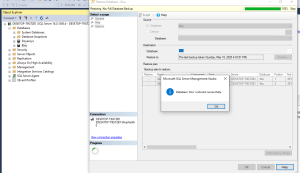
Restore from Backup
If necessary, restore the database using a recent backup to recover from the issue.
Conclusion:
SUSPECT and RECOVERY PENDING states signal serious issues that block database access. Quick diagnosis, proper repair steps, and reliable backups are essential to restore availability while minimizing data loss.
