Oracle LogMiner: Unlocking the Power of Database Transaction Analysis
In the world of database management, understanding the changes happening inside your Oracle Database is crucial. Whether it’s for auditing, troubleshooting, or replicating data, having a detailed insight into transaction-level changes can be a gamechanger. This is where Oracle LogMiner comes in.
What is Oracle LogMiner?
Oracle LogMiner is a utility provided by Oracle that allows you to query redo log files to track changes made to the database. Essentially, it gives you a way to “look back in time” at every insert, update, and delete operation performed on your tables. LogMiner is commonly used for:
- Auditing database changes
- Data replication and synchronization
- Recovering from accidental DML operations
- Monitoring application activity
How LogMiner Works
Oracle databases record every change in redo logs. These logs capture all modifications made to the database, including:
- INSERT statements
- UPDATE statements
- DELETE statements
LogMiner reads these redo logs and provides SQL-level representations of the changes. This makes it easier for DBAs and developers to analyze and even replay transactions if necessary.
Key Features of LogMiner
- SQL-Level Change Analysis
LogMiner reconstructs DML operations from redo logs, so you see the actual SQL statements executed.
- Flexible Log Sources
You can analyze both online redo logs and archived logs, giving you flexibility in tracking historical changes.
- Fine-Grained Filtering
LogMiner lets you filter changes based on schema, table, or even transaction ID, helping to focus on the data you care about.
- Integration with PL/SQL
You can query LogMiner directly using SQL and PL/SQL, making it easy to automate auditing and reporting tasks.
Steps to Use LogMiner
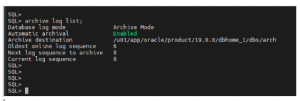
Step 1: Check ARCHIVELOG Mode
SQL> ARCHIVE LOG LIST;
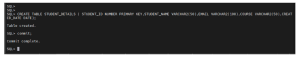
Step 2: Create Sample Table
CREATE TABLE student_details (
student_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
student_name VARCHAR2(50),
email VARCHAR2(100),
course VARCHAR2(50),
created_date DATE
);
COMMIT;
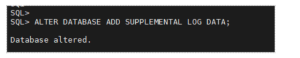
Step 3: Enable Supplemental Logging
Supplemental logging is required to capture enough information for LogMiner to reconstruct SQL statements:
ALTER DATABASE ADD SUPPLEMENTAL LOG DATA;
![]()
Step 4: Perform DML on STUDENT_DETAILS
INSERT
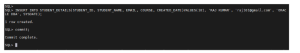
DELETE
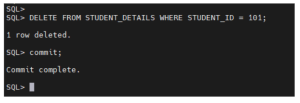
Step 5: Identify Archive Log Files
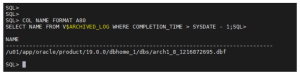
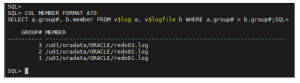
Step 6: Identify Redo Log Files
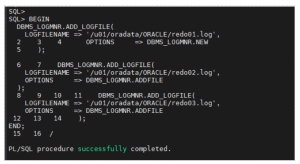
Step 7: Start LogMiner Session
Specify the redo logs you want to analyze:
Step 8: Start LogMiner
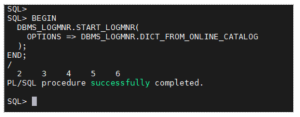
Step 9: Query LogMiner Output

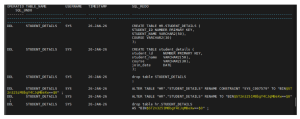
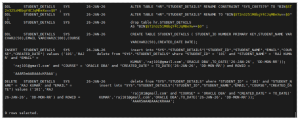
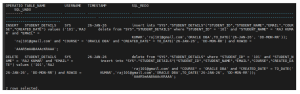
Step 10: Stop LogMiner
Conclusion
Oracle LogMiner is an essential tool for DBAs to analyze redo logs and audit database activity without restoring backups. In this walkthrough, we demonstrated how to configure LogMiner, perform DML operations, and retrieve readable SQL statements using SQL_REDO and SQL_UNDO. With proper formatting and logging enabled, LogMiner provides clear visibility into database changes, making it invaluable for troubleshooting, compliance, and recovery scenarios.
