SQL Server Index Maintenance: Improving Query Performance
PURPOSE AND SCOPE
This document explains the importance of index maintenance in SQL Server and demonstrates how to identify and resolve index fragmentation issues to improve query performance and overall database efficiency.
PREREQUISITES
-
Access to SQL Server with appropriate database permissions
-
Basic understanding of SQL Server indexes
-
Recommended to perform activities during a maintenance window
-
Ensure recent database backup is available
INTRODUCTION
Indexes play a crucial role in improving query performance in SQL Server. Over time, frequent INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations cause index fragmentation, which can negatively impact performance. Regular index maintenance helps maintain optimal database performance.
TYPES OF INDEX FRAGMENTATION
-
Logical Fragmentation– Pages are out of order, affecting scan performance
-
Internal Fragmentation– Pages have unused space, leading to inefficient storage
PROCEDURE
Step 1: Check Index Fragmentation
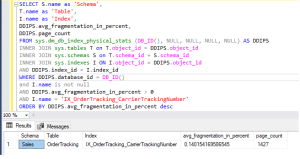
Use the following query to identify fragmented indexes:
SELECT S.name as ‘Schema’,
T.name as ‘Table’,
I.name as ‘Index’,
DDIPS.avg_fragmentation_in_percent,
DDIPS.page_count
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL) AS DDIPS
INNER JOIN sys.tables T on T.object_id = DDIPS.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.schemas S on T.schema_id = S.schema_id
INNER JOIN sys.indexes I ON I.object_id = DDIPS.object_id
AND DDIPS.index_id = I.index_id
WHERE DDIPS.database_id = DB_ID()
and I.name is not null
AND DDIPS.avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 0
ORDER BY DDIPS.avg_fragmentation_in_percent desc
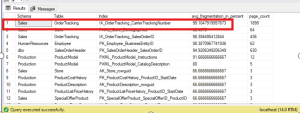
Step 2: Decide Maintenance Action
Fragmentation Level |
Recommended Action |
10% – 30% |
Reorganize Index |
Above 30% |
Rebuild Index |
Step 3: Reorganize Index
Reorganizing is an online operation and does not block users:
ALTER INDEX index_nameON table_name
REORGANIZE;
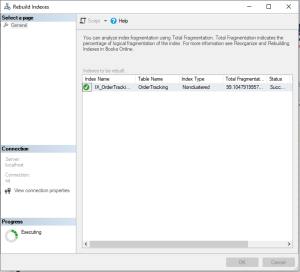
Step 4: Rebuild Index
Rebuilding recreates the index and improves performance significantly.
REBUILD Index can be set online or offline using the below SQL commands:
ALTER INDEX Index_Name ON Table_Name REBUILD
–REBUILD Index with ONLINE OPTION
ALTER INDEX Index_Name ON Table_Name REBUILD WITH(ONLINE=ON) | WITH(ONLINE=ON)
(Or)
Find and expand the table in Object Explorer >> Open Indexes >> Right-click on the target index >> Rebuild or Reorganize.
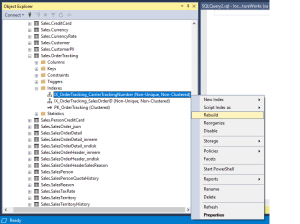
Note: Index rebuilds are resource-intensive and may cause blocking in Standard Edition.
Step 5: Update Statistics
After rebuilding indexes, update statistics to ensure the query optimizer uses the latest data distribution:
UPDATE STATISTICS table_name;
BEST PRACTICES
-
Schedule index maintenance during low-usage hours
-
Monitor fragmentation regularly
-
Avoid rebuilding indexes unnecessarily
-
Use maintenance plans or SQL Agent jobs for automation
CONCLUSION
Regular index maintenance is essential for maintaining SQL Server performance and stability. By monitoring fragmentation levels and applying appropriate actions such as reorganizing or rebuilding indexes, database performance can be significantly improved. Implementing a consistent maintenance strategy ensures efficient query execution and long-term database health.