1. Overview
This document will be helpful to upload a excel file directly and view it as a report.
2. Technologies and Tools Used
- Oracle Plsql.
3. Use Case
Customer wants to upload a excel file and view it as a report.
4. Architecture
We can achieve this by using below simple method.
Steps to follow.
Step:1
Create a region and File browser item as PX_XLSX_FILE.
Step:2
Set PX_XLSX_FILE item Setting .
storage type : APEX_APPLICATION_TEMP_FILES
Purge File at : End of Session.
Code:
Run the below plsql object.
create or replace package body xlsx_parser is
g_worksheets_path_prefix constant varchar2(14) := ‘xl/worksheets/’;
–==================================================================================================================
function get_date( p_xlsx_date_number in number ) return date is
begin
return
case when p_xlsx_date_number > 61
then DATE’1900-01-01′ – 2 + p_xlsx_date_number
else DATE’1900-01-01′ – 1 + p_xlsx_date_number
end;
end get_date;
–==================================================================================================================
procedure get_blob_content(
p_xlsx_name in varchar2,
p_xlsx_content in out nocopy blob )
is
begin
if p_xlsx_name is not null then
select blob_content into p_xlsx_content
from apex_application_temp_files
where name = p_xlsx_name;
end if;
exception
when no_data_found then
null;
end get_blob_content;
–==================================================================================================================
function extract_worksheet(
p_xlsx in blob,
p_worksheet_name in varchar2 ) return blob
is
l_worksheet blob;
begin
if p_xlsx is null or p_worksheet_name is null then
return null;
end if;
l_worksheet := apex_zip.get_file_content(
p_zipped_blob => p_xlsx,
p_file_name => g_worksheets_path_prefix || p_worksheet_name || ‘.xml’ );
if l_worksheet is null then
raise_application_error(-20000, ‘WORKSHEET “‘ || p_worksheet_name || ‘” DOES NOT EXIST’);
end if;
return l_worksheet;
end extract_worksheet;
–==================================================================================================================
procedure extract_shared_strings(
p_xlsx in blob,
p_strings in out nocopy wwv_flow_global.vc_arr2 )
is
l_shared_strings blob;
begin
l_shared_strings := apex_zip.get_file_content(
p_zipped_blob => p_xlsx,
p_file_name => ‘xl/sharedStrings.xml’ );
if l_shared_strings is null then
return;
end if;
select shared_string
bulk collect into p_strings
from xmltable(
xmlnamespaces( default ‘http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/spreadsheetml/2006/main’ ),
‘//si’
passing xmltype.createxml( l_shared_strings, nls_charset_id(‘AL32UTF8’), null )
columns
shared_string varchar2(4000) path ‘t/text()’ );
end extract_shared_strings;
–==================================================================================================================
procedure extract_date_styles(
p_xlsx in blob,
p_format_codes in out nocopy wwv_flow_global.vc_arr2 )
is
l_stylesheet blob;
begin
l_stylesheet := apex_zip.get_file_content(
p_zipped_blob => p_xlsx,
p_file_name => ‘xl/styles.xml’ );
if l_stylesheet is null then
return;
end if;
select lower( n.formatCode )
bulk collect into p_format_codes
from
xmltable(
xmlnamespaces( default ‘http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/spreadsheetml/2006/main’ ),
‘//cellXfs/xf’
passing xmltype.createxml( l_stylesheet, nls_charset_id(‘AL32UTF8’), null )
columns
numFmtId number path ‘@numFmtId’ ) s,
xmltable(
xmlnamespaces( default ‘http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/spreadsheetml/2006/main’ ),
‘//numFmts/numFmt’
passing xmltype.createxml( l_stylesheet, nls_charset_id(‘AL32UTF8’), null )
columns
formatCode varchar2(255) path ‘@formatCode’,
numFmtId number path ‘@numFmtId’ ) n
where s.numFmtId = n.numFmtId ( + );
end extract_date_styles;
–==================================================================================================================
function convert_ref_to_col#( p_col_ref in varchar2 ) return pls_integer is
l_colpart varchar2(10);
l_linepart varchar2(10);
begin
l_colpart := replace(translate(p_col_ref,’1234567890′,’__________’), ‘_’);
if length( l_colpart ) = 1 then
return ascii( l_colpart ) – 64;
else
return ( ascii( substr( l_colpart, 1, 1 ) ) – 64 ) * 26 + ( ascii( substr( l_colpart, 2, 1 ) ) – 64 );
end if;
end convert_ref_to_col#;
–==================================================================================================================
procedure reset_row( p_parsed_row in out nocopy xlsx_row_t ) is
begin
— reset row
p_parsed_row.col01 := null; p_parsed_row.col02 := null; p_parsed_row.col03 := null; p_parsed_row.col04 := null; p_parsed_row.col05 := null;
p_parsed_row.col06 := null; p_parsed_row.col07 := null; p_parsed_row.col08 := null; p_parsed_row.col09 := null; p_parsed_row.col10 := null;
p_parsed_row.col11 := null; p_parsed_row.col12 := null; p_parsed_row.col13 := null; p_parsed_row.col14 := null; p_parsed_row.col15 := null;
p_parsed_row.col16 := null; p_parsed_row.col17 := null; p_parsed_row.col18 := null; p_parsed_row.col19 := null; p_parsed_row.col20 := null;
p_parsed_row.col21 := null; p_parsed_row.col22 := null; p_parsed_row.col23 := null; p_parsed_row.col24 := null; p_parsed_row.col25 := null;
p_parsed_row.col26 := null; p_parsed_row.col27 := null; p_parsed_row.col28 := null; p_parsed_row.col29 := null; p_parsed_row.col30 := null;
p_parsed_row.col31 := null; p_parsed_row.col32 := null; p_parsed_row.col33 := null; p_parsed_row.col34 := null; p_parsed_row.col35 := null;
p_parsed_row.col36 := null; p_parsed_row.col37 := null; p_parsed_row.col38 := null; p_parsed_row.col39 := null; p_parsed_row.col40 := null;
p_parsed_row.col41 := null; p_parsed_row.col42 := null; p_parsed_row.col43 := null; p_parsed_row.col44 := null; p_parsed_row.col45 := null;
p_parsed_row.col46 := null; p_parsed_row.col47 := null; p_parsed_row.col48 := null; p_parsed_row.col49 := null; p_parsed_row.col50 := null;
end reset_row;
–==================================================================================================================
function parse(
p_xlsx_name in varchar2 default null,
p_xlsx_content in blob default null,
p_worksheet_name in varchar2 default ‘sheet1’,
p_max_rows in number default 1000000 ) return xlsx_tab_t pipelined
is
l_worksheet blob;
l_xlsx_content blob;
l_shared_strings wwv_flow_global.vc_arr2;
l_format_codes wwv_flow_global.vc_arr2;
l_parsed_row xlsx_row_t;
l_first_row boolean := true;
l_value varchar2(32767);
l_line# pls_integer := 1;
l_real_col# pls_integer;
l_row_has_content boolean := false;
begin
if p_xlsx_content is null then
get_blob_content( p_xlsx_name, l_xlsx_content );
else
l_xlsx_content := p_xlsx_content;
end if;
if l_xlsx_content is null then
return;
end if;
l_worksheet := extract_worksheet(
p_xlsx => l_xlsx_content,
p_worksheet_name => p_worksheet_name );
extract_shared_strings(
p_xlsx => l_xlsx_content,
p_strings => l_shared_strings );
extract_date_styles(
p_xlsx => l_xlsx_content,
p_format_codes => l_format_codes );
— the actual XML parsing starts here
for i in (
select
r.xlsx_row,
c.xlsx_col#,
c.xlsx_col,
c.xlsx_col_type,
c.xlsx_col_style,
c.xlsx_val
from xmltable(
xmlnamespaces( default ‘http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/spreadsheetml/2006/main’ ),
‘//row’
passing xmltype.createxml( l_worksheet, nls_charset_id(‘AL32UTF8’), null )
columns
xlsx_row number path ‘@r’,
xlsx_cols xmltype path ‘.’
) r, xmltable (
xmlnamespaces( default ‘http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/spreadsheetml/2006/main’ ),
‘//c’
passing r.xlsx_cols
columns
xlsx_col# for ordinality,
xlsx_col varchar2(15) path ‘@r’,
xlsx_col_type varchar2(15) path ‘@t’,
xlsx_col_style varchar2(15) path ‘@s’,
xlsx_val varchar2(4000) path ‘v/text()’
) c
where p_max_rows is null or r.xlsx_row <= p_max_rows
) loop
if i.xlsx_col# = 1 then
l_parsed_row.line# := l_line#;
if not l_first_row then
pipe row( l_parsed_row );
l_line# := l_line# + 1;
reset_row( l_parsed_row );
l_row_has_content := false;
else
l_first_row := false;
end if;
end if;
if i.xlsx_col_type = ‘s’ then
if l_shared_strings.exists( i.xlsx_val + 1) then
l_value := l_shared_strings( i.xlsx_val + 1);
else
l_value := ‘[Data Error: N/A]’ ;
end if;
else
if l_format_codes.exists( i.xlsx_col_style + 1 ) and (
instr( l_format_codes( i.xlsx_col_style + 1 ), ‘d’ ) > 0 and
instr( l_format_codes( i.xlsx_col_style + 1 ), ‘m’ ) > 0 )
then
l_value := to_char( get_date( i.xlsx_val ), c_date_format );
else
l_value := i.xlsx_val;
end if;
end if;
pragma inline( convert_ref_to_col#, ‘YES’ );
l_real_col# := convert_ref_to_col#( i.xlsx_col );
if l_real_col# between 1 and 50 then
l_row_has_content := true;
end if;
— we currently support 50 columns – but this can easily be increased. Just add additional lines
— as follows:
— when l_real_col# = {nn} then l_parsed_row.col{nn} := l_value;
case
when l_real_col# = 1 then l_parsed_row.col01 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 2 then l_parsed_row.col02 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 3 then l_parsed_row.col03 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 4 then l_parsed_row.col04 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 5 then l_parsed_row.col05 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 6 then l_parsed_row.col06 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 7 then l_parsed_row.col07 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 8 then l_parsed_row.col08 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 9 then l_parsed_row.col09 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 10 then l_parsed_row.col10 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 11 then l_parsed_row.col11 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 12 then l_parsed_row.col12 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 13 then l_parsed_row.col13 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 14 then l_parsed_row.col14 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 15 then l_parsed_row.col15 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 16 then l_parsed_row.col16 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 17 then l_parsed_row.col17 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 18 then l_parsed_row.col18 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 19 then l_parsed_row.col19 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 20 then l_parsed_row.col20 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 21 then l_parsed_row.col21 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 22 then l_parsed_row.col22 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 23 then l_parsed_row.col23 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 24 then l_parsed_row.col24 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 25 then l_parsed_row.col25 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 26 then l_parsed_row.col26 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 27 then l_parsed_row.col27 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 28 then l_parsed_row.col28 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 29 then l_parsed_row.col29 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 30 then l_parsed_row.col30 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 31 then l_parsed_row.col31 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 32 then l_parsed_row.col32 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 33 then l_parsed_row.col33 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 34 then l_parsed_row.col34 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 35 then l_parsed_row.col35 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 36 then l_parsed_row.col36 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 37 then l_parsed_row.col37 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 38 then l_parsed_row.col38 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 39 then l_parsed_row.col39 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 40 then l_parsed_row.col40 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 41 then l_parsed_row.col41 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 42 then l_parsed_row.col42 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 43 then l_parsed_row.col43 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 44 then l_parsed_row.col44 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 45 then l_parsed_row.col45 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 46 then l_parsed_row.col46 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 47 then l_parsed_row.col47 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 48 then l_parsed_row.col48 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 49 then l_parsed_row.col49 := l_value;
when l_real_col# = 50 then l_parsed_row.col50 := l_value;
else null;
end case;
end loop;
if l_row_has_content then
l_parsed_row.line# := l_line#;
pipe row( l_parsed_row );
end if;
return;
end parse;
–==================================================================================================================
function get_worksheets(
p_xlsx_content in blob default null,
p_xlsx_name in varchar2 default null ) return apex_t_varchar2 pipelined
is
l_zip_files apex_zip.t_files;
l_xlsx_content blob;
begin
if p_xlsx_content is null then
get_blob_content( p_xlsx_name, l_xlsx_content );
else
l_xlsx_content := p_xlsx_content;
end if;
l_zip_files := apex_zip.get_files(
p_zipped_blob => l_xlsx_content );
for i in 1 .. l_zip_files.count loop
if substr( l_zip_files( i ), 1, length( g_worksheets_path_prefix ) ) = g_worksheets_path_prefix then
pipe row( rtrim( substr( l_zip_files ( i ), length( g_worksheets_path_prefix ) + 1 ), ‘.xml’ ) );
end if;
end loop;
return;
end get_worksheets;
end xlsx_parser;
Step:3
Create a button as Submit in File browser region.
Step:4
Create a Classic report region with sql code as
Code:
select *
from table( xlsx_parser.parse(
p_xlsx_name => :PX_XLSX_FILE ) )
where line# != 1
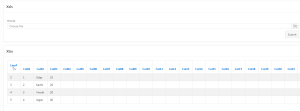
1. Screen Shot
Output:
Excel input file content
| Sno | Name | Id |
| 1 | Uday | 10 |
| 2 | Karthi | 20 |
| 3 | Vinoth | 30 |
| 4 | Jegan | 40 |
Source Link: https://blogs.oracle.com/apex/easy-xlsx-parser:-just-with-sql-and-plsql
