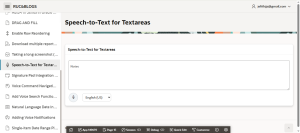
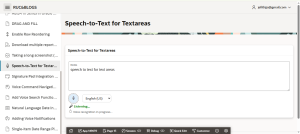
Introduction: –
In the modern digital age, enabling voice input is a great way to enhance user experience, especially for accessibility and convenience. With the advancement in browser-based APIs, integrating Speech-to-Text into Oracle APEX textareas can significantly reduce the manual effort in data entry and improve application usability.
The following technologies have been used in speech to text in Oracle APEX.
- Oracle APEX
- HTML
- Javascript
Why we need to do: –
Typing long notes or detailed information into a form can be time-consuming and challenging for users, especially on mobile devices. By integrating voice input directly into Oracle APEX textareas, we make it easier for users to speak their input, which is then automatically transcribed into text. This is particularly useful for support applications, reporting tools, and accessibility enhancements.
How do we solve:
Step 1 :Add the following Region HTML to your page:
<!-- Microphone Button --> <button type="button" id="start-speech" class="t-Button t-Button--noLabel" title="Start Voice Input"> <span class="fa fa-microphone"></span> </button> <!-- Language Selector --> <select id="speech-lang" class="t-Form-select"> <option value="en-US">English (US)</option> <option value="en-IN">English (India)</option> <option value="en-GB">English (UK)</option> </select> <!-- Listening Message --> <div id="listening-msg" style="display:none; color: green; font-weight: bold; margin-top: 5px;"> </div> <!-- Spinner --> <div id="speech-status" style="display:none; margin-top: 5px;"><span class="fa fa-spinner fa-spin"></span> Voice recognition in progress... </div>
Step 2: Add this JavaScript code in ‘Execute when Page Loads’ section
document.getElementById("start-speech").addEventListener("click", function () {
try {
const SpeechRecognition = window.SpeechRecognition || window.webkitSpeechRecognition;
if (!SpeechRecognition) {
alert("Speech Recognition is not supported in this browser.");
return;
}
const recognition = new SpeechRecognition();
const langSelect = document.getElementById("speech-lang");
recognition.lang = langSelect.value;
recognition.interimResults = false;
recognition.maxAlternatives = 1;
document.getElementById("speech-status").style.display = "block";
document.getElementById("listening-msg").style.display = "block";
recognition.start();
recognition.onresult = function (event) {
const speechResult = event.results[0][0].transcript;
const currentText = $v("P15_NOTES");
$s("P15_NOTES", currentText + " " + speechResult);
};
recognition.onerror = function (event) {
console.error("Speech recognition error", event.error);
alert("Error during speech recognition: " + event.error);
};
recognition.onend = function () {
document.getElementById("speech-status").style.display = "none";
document.getElementById("listening-msg").style.display = "none";
};
} catch (e) {
console.error("Speech recognition not supported", e);
}
});
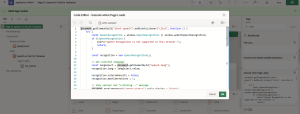
Conclusion:
Speech-to-Text integration in Oracle APEX enhances user experience, especially in applications where quick and hands-free data entry is required. With just a few lines of JavaScript and HTML, developers can leverage browser capabilities to make their APEX applications more accessible and modern.